The vasorelaxant effect of H(2)S as a novel endogenous gaseous K(ATP) channel opener
- PMID: 11689441
- PMCID: PMC125693
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/20.21.6008
The vasorelaxant effect of H(2)S as a novel endogenous gaseous K(ATP) channel opener
Abstract
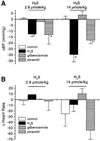
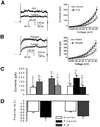
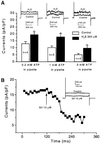
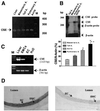
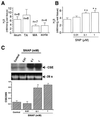
Hydrogen sulfide (H(2)S) has been traditionally viewed as a toxic gas. It is also, however, endogenously generated from cysteine metabolism. We attempted to assess the physiological role of H(2)S in the regulation of vascular contractility, the modulation of H(2)S production in vascular tissues, and the underlying mechanisms. Intravenous bolus injection of H(2)S transiently decreased blood pressure of rats by 12- 30 mmHg, which was antagonized by prior blockade of K(ATP) channels. H(2)S relaxed rat aortic tissues in vitro in a K(ATP) channel-dependent manner. In isolated vascular smooth muscle cells (SMCs), H(2)S directly increased K(ATP) channel currents and hyperpolarized membrane. The expression of H(2)S-generating enzyme was identified in vascular SMCs, but not in endothelium. The endogenous production of H(2)S from different vascular tissues was also directly measured with the abundant level in the order of tail artery, aorta and mesenteric artery. Most importantly, H(2)S production from vascular tissues was enhanced by nitric oxide. Our results demonstrate that H(2)S is an important endogenous vasoactive factor and the first identified gaseous opener of K(ATP) channels in vascular SMCs.
Figures


References
-
- Doughty J.M., Plane,F. and Langton,P.D. (1999) Charybdotoxin and apamin block EDHF in rat mesenteric artery if selectively applied to the endothelium. Am. J. Physiol., 276, H1107–H1112. - PubMed
-
- Hattori Y., Kawasaki,H., Fukao,M. and Kanno,M. (1995) Phorbol esters elicit Ca2+-dependent delayed contractions in diabetic rat aorta. Eur. J. Pharmacol., 279, 51–58. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

