Mechanism for the switch of phi29 DNA early to late transcription by regulatory protein p4 and histone-like protein p6
- PMID: 11689446
- PMCID: PMC125705
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/20.21.6060
Mechanism for the switch of phi29 DNA early to late transcription by regulatory protein p4 and histone-like protein p6
Abstract
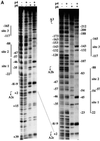
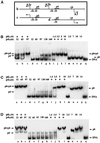
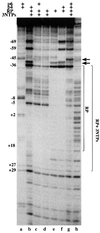
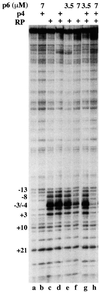
Bacteriophage phi29 gene expression takes place from four major promoters, three of them (A2b, A2c and A3) clustered within 219 bp at a central region of the genome. Transcription regulation of these promoters involves both a highly specific DNA-binding protein (p4) and a low specificity DNA-binding protein (p6) functionally related to prokaryotic histone-like proteins. Protein p6 forms extended oligomeric arrays along the phage DNA. In contrast, protein p4 binds specifically upstream of late promoter A3 and early promoter A2c. We have analysed the concomitant binding of p6 and p4 and found that the proteins cooperate with each other in the binding to the central region of the genome, resulting in a ternary p4-p6-DNA complex that affects local DNA topology. Through this complex, protein p6 exerts a direct role in the repression of promoter A2c, impeding unwinding of the DNA strands needed for open complex formation. In contrast, protein p6 functions by reinforcing the positioning of protein p4 in the repression of promoter A2b and activation of promoter A3, thereby facilitating p4-mediated transcription regulation.
Figures






References
-
- Adhya S., Geanacopoulos,M., Lewis,D.E., Roy,S. and Aki,T. (1998) Transcription regulation by repressosome and by RNA polymerase contact. Cold Spring Harbor Symp. Quant. Biol., 63, 1–9. - PubMed
-
- Afflerbach H., Schröder,O. and Wagner,R. (1999) Conformational changes of the upstream DNA mediated by H-NS and FIS regulate E.coli rrnB P1 promoter activity. J. Mol. Biol., 286, 339–353. - PubMed
-
- Barthelemy I. and Salas,M. (1989) Characterization of a new prokaryotic transcriptional activator and its DNA recognition site. J. Mol. Biol., 208, 225–232. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

