Critical roles of nuclear receptor response elements in replication of hepatitis B virus
- PMID: 11689616
- PMCID: PMC114721
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.75.23.11354-11364.2001
Critical roles of nuclear receptor response elements in replication of hepatitis B virus
Abstract
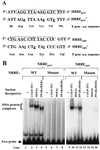
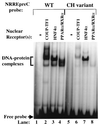
Functional analysis of the roles of the nuclear receptor response elements (NRREs) in the transcription and replication of hepatitis B virus (HBV) in the context of its whole genome has been hampered by the extensive overlapping of the NRREs with the regions encoding viral proteins. We introduced point mutations that inactivate the NRREs individually without altering the open reading frames of viral proteins. These mutations in the context of a plasmid containing 1.2 copies of the HBV genome were transiently transfected into the human hepatoma cell line Huh7. Inactivation of the NRRE in either the preC promoter (NRRE(preC)) or enhancer I (NRRE(enhI)) led to moderate reductions in synthesis of viral RNAs. Concurrent inactivation of both NRREs led to 7- to 8-fold reductions in synthesis of the preC, pregenomic, and preS RNAs and a 15-fold reduction in synthesis of the S RNA. The accumulation of viral DNA in the cytoplasmic nucleocapsids and virion particles in the culture medium was also reduced seven- to eightfold. These results suggest that these NRREs are critical for the efficient propagation of HBV in hepatocytes. In cotransfection experiments we also found that overexpression of PPARalpha-RXRalpha in the presence of their respective ligands led to a fourfold increase in pregenomic RNA synthesis and a four- to fivefold increase in viral DNA synthesis, while it had little or no effect on synthesis of the other viral RNAs. Similar effects were observed with overexpression of PPARgamma-RXRalpha in the presence of their respective ligands. This activation was dependent on NRRE(preC), because the increase in synthesis of viral RNA and DNA was not observed when this site was mutated. Likewise, no activation of synthesis of pregenomic RNA and viral DNA by PPARalpha-RXRalpha was observed in a naturally occurring NRRE(preC)(-) mutant of HBV. Our results suggest that interactions between nuclear receptors and NRREs present in the HBV genome may play critical roles in regulating its transcription and replication during HBV infection of hepatocytes.
Figures

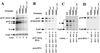


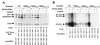
Similar articles
-
Distinct modes of regulation of transcription of hepatitis B virus by the nuclear receptors HNF4alpha and COUP-TF1.J Virol. 2003 Feb;77(4):2489-99. doi: 10.1128/jvi.77.4.2489-2499.2003. J Virol. 2003. PMID: 12551987 Free PMC article.
-
Differential regulation of the pre-C and pregenomic promoters of human hepatitis B virus by members of the nuclear receptor superfamily.J Virol. 1997 Dec;71(12):9366-74. doi: 10.1128/JVI.71.12.9366-9374.1997. J Virol. 1997. PMID: 9371596 Free PMC article.
-
Transcription and replication of a natural hepatitis B virus nucleocapsid promoter variant is regulated in vivo by peroxisome proliferators.Virology. 2001 Oct 25;289(2):239-51. doi: 10.1006/viro.2001.1169. Virology. 2001. PMID: 11689047
-
Molecular biology of the hepatitis B virus and role of the X gene.Pathol Biol (Paris). 2010 Aug;58(4):267-72. doi: 10.1016/j.patbio.2010.03.005. Epub 2010 May 18. Pathol Biol (Paris). 2010. PMID: 20483545 Review.
-
Hepatitis B virus reverse transcriptase and its many roles in hepadnaviral genomic replication.Infect Agents Dis. 1994 Apr-Jun;3(2-3):85-93. Infect Agents Dis. 1994. PMID: 7529120 Review.
Cited by
-
MicroRNA-130a can inhibit hepatitis B virus replication via targeting PGC1α and PPARγ.RNA. 2015 Mar;21(3):385-400. doi: 10.1261/rna.048744.114. Epub 2015 Jan 16. RNA. 2015. PMID: 25595716 Free PMC article.
-
Distinct modes of regulation of transcription of hepatitis B virus by the nuclear receptors HNF4alpha and COUP-TF1.J Virol. 2003 Feb;77(4):2489-99. doi: 10.1128/jvi.77.4.2489-2499.2003. J Virol. 2003. PMID: 12551987 Free PMC article.
-
Genome replication, virion secretion, and e antigen expression of naturally occurring hepatitis B virus core promoter mutants.J Virol. 2003 Jun;77(12):6601-12. doi: 10.1128/jvi.77.12.6601-6612.2003. J Virol. 2003. PMID: 12767980 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-141 represses HBV replication by targeting PPARA.PLoS One. 2012;7(3):e34165. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0034165. Epub 2012 Mar 30. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22479552 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptional and posttranscriptional control of hepatitis B virus gene expression.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003 Feb 4;100(3):1310-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.252773599. Epub 2003 Jan 27. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003. PMID: 12552098 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Brown T. Southern blotting. In: Ausubel F M, Brent R, Kingston R E, Moore D D, Seidman J G, Smith J A, Struhl K, editors. Current protocols in molecular biology. New York, N.Y: John Wiley and Sons, Inc.; 1993. p. 2.9.1.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

