Role of matrix and fusion proteins in budding of Sendai virus
- PMID: 11689619
- PMCID: PMC114724
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.75.23.11384-11391.2001
Role of matrix and fusion proteins in budding of Sendai virus
Abstract
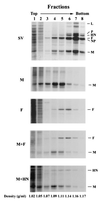
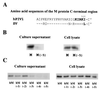
Paramyxoviruses are assembled at the surface of infected cells, where virions are formed by the process of budding. We investigated the roles of three Sendai virus (SV) membrane proteins in the production of virus-like particles. Expression of matrix (M) proteins from cDNA induced the budding and release of virus-like particles that contained M, as was previously observed with human parainfluenza virus type 1 (hPIV1). Expression of SV fusion (F) glycoprotein from cDNA caused the release of virus-like particles bearing surface F, although their release was less efficient than that of particles bearing M protein. Cells that expressed only hemagglutinin-neuraminidase (HN) released no HN-containing vesicles. Coexpression of M and F proteins enhanced the release of F protein by a factor greater than 4. The virus-like particles containing F and M were found in different density gradient fractions of the media of cells that coexpressed M and F, a finding that suggests that the two proteins formed separate vesicles and did not interact directly. Vesicles released by M or F proteins also contained cellular actin; therefore, actin may be involved in the budding process induced by viral M or F proteins. Deletion of C-terminal residues of M protein, which has a sequence similar to that of an actin-binding domain, significantly reduced release of the particles into medium. Site-directed mutagenesis of the cytoplasmic tail of F revealed two regions that affect the efficiency of budding: one domain comprising five consecutive amino acids conserved in SV and hPIV1 and one domain that is similar to the actin-binding domain required for budding induced by M protein. Our results indicate that both M and F proteins are able to drive the budding of SV and propose the possible role of actin in the budding process.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Requirements for budding of paramyxovirus simian virus 5 virus-like particles.J Virol. 2002 Apr;76(8):3952-64. doi: 10.1128/jvi.76.8.3952-3964.2002. J Virol. 2002. PMID: 11907235 Free PMC article.
-
The YLDL sequence within Sendai virus M protein is critical for budding of virus-like particles and interacts with Alix/AIP1 independently of C protein.J Virol. 2007 Mar;81(5):2263-73. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02218-06. Epub 2006 Dec 13. J Virol. 2007. PMID: 17166905 Free PMC article.
-
Assembly of Sendai virus: M protein interacts with F and HN proteins and with the cytoplasmic tail and transmembrane domain of F protein.Virology. 2000 Oct 25;276(2):289-303. doi: 10.1006/viro.2000.0556. Virology. 2000. PMID: 11040121
-
[Envelope virus assembly and budding].Uirusu. 2010 Jun;60(1):105-13. doi: 10.2222/jsv.60.105. Uirusu. 2010. PMID: 20848870 Review. Japanese.
-
Molecular mechanism of paramyxovirus budding.Virus Res. 2004 Dec;106(2):133-45. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2004.08.010. Virus Res. 2004. PMID: 15567493 Review.
Cited by
-
Packaging of actin into Ebola virus VLPs.Virol J. 2005 Dec 20;2:92. doi: 10.1186/1743-422X-2-92. Virol J. 2005. PMID: 16367999 Free PMC article.
-
C Proteins: Controllers of Orderly Paramyxovirus Replication and of the Innate Immune Response.Viruses. 2022 Jan 12;14(1):137. doi: 10.3390/v14010137. Viruses. 2022. PMID: 35062341 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Different regions of the newcastle disease virus fusion protein modulate pathogenicity.PLoS One. 2014 Dec 1;9(12):e113344. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0113344. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25437176 Free PMC article.
-
Nipah virus matrix protein: expert hacker of cellular machines.FEBS Lett. 2016 Aug;590(15):2494-511. doi: 10.1002/1873-3468.12272. Epub 2016 Jul 12. FEBS Lett. 2016. PMID: 27350027 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mutation of the TYTLE motif in the cytoplasmic tail of the sendai virus fusion protein deeply affects viral assembly and particle production.PLoS One. 2013 Dec 10;8(12):e78074. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0078074. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24339863 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ali A, Nayak D P. Assembly of Sendai virus: M protein interacts with F and HN proteins and with the cytoplasmic tail and transmembrane domain of F protein. Virology. 2000;276:289–303. - PubMed
-
- Bohn W, Rutter G, Hohenberg H, Mannweiler K, Nobis P. Involvement of actin filaments in budding of measles virus: studies on cytoskeletons of infected cells. Virology. 1986;149:91–106. - PubMed
-
- Bousse T, Takimoto T, Gorman W L, Takahashi T, Portner A. Regions on the hemagglutinin-neuraminidase proteins of human parainfluenza virus type-1 and Sendai virus important for membrane fusion. Virology. 1994;204:506–514. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

