Early and persistent bone marrow hematopoiesis defect in simian/human immunodeficiency virus-infected macaques despite efficient reduction of viremia by highly active antiretroviral therapy during primary infection
- PMID: 11689641
- PMCID: PMC114746
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.75.23.11594-11602.2001
Early and persistent bone marrow hematopoiesis defect in simian/human immunodeficiency virus-infected macaques despite efficient reduction of viremia by highly active antiretroviral therapy during primary infection
Abstract
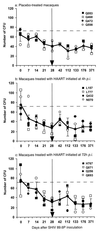
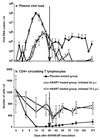
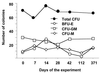
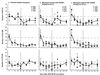
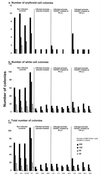
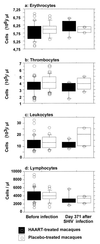
The hematological abnormalities observed in human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-infected patients appear to be mainly due to bone marrow dysfunction. A macaque models of AIDS could greatly facilitate an in vivo approach to the pathogenesis of such dysfunction. Here, we evaluated in this model the impact of infection with a pathogenic simian/human immunodeficiency virus (SHIV) on bone marrow hematopoiesis. Three groups of macaques were inoculated with 50 50% median infective doses of pathogenic SHIV 89.P, which expresses env of dual-tropic HIV type 1 (HIV-1) 89.6 primary isolate. During the primary phase of infection, animals were treated with either a placebo or highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART) combining zidovudine, lamivudine, and indinavir, initiated 4 or 72 h postinfection (p.i.) and administered twice a day until day 28 p.i. In both placebo-treated and HAART-treated animals, bone marrow colony-forming cells (CFC) progressively decreased quite early, during the first month p.i. One year p.i., both placebo- and HAART-treated animals displayed decreases in CFC to about 56% of preinfection values. At the same time, a dramatic decrease (greater than 77%) of bone marrow CD34(+) long-term culture-initiating cells was noted in all animals were found. No statistically significant differences between placebo- and HAART-treated monkeys were found. These data argue for an early and profound alteration of myelopoiesis at the level of the most primitive CD34(+) progenitor cells during SHIV infection, independently of the level of viremia, circulating CD4(+) cell counts, or antiviral treatment.
Figures
References
-
- Adams G B, Pym A S, Poznansky M C, McClure M O, Weber J N. The in vivo effects of combination antiretroviral drug therapy on peripheral blood CD34+ cell colony-forming units from HIV type 1-infected patients. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1999;15:551–559. - PubMed
-
- Aiuti A, Turchetto L, Cota M, Cipponi A, Brambilla A, Arcelloni C, Paroni R, Vicenzi E, Bordignon C, Poli G. Human CD34(+) cells express CXCR4 and its ligand stromal cell-derived factor-1. Implications for infection by T-cell tropic human immunodeficiency virus. Blood. 1999;94:62–73. - PubMed
-
- Brogan K L, Zell S C. Hematologic toxicity of zidovudine in HIV-infected patients. Am Fam Physician. 1990;41:1521–1528. - PubMed
-
- Broxmeyer H E, Sherry B, Cooper S, Lu L, Maze R, Beckmann M P, Cerami A, Ralph P. Comparative analysis of the human macrophage inflammatory protein family of cytokines (chemokines) on proliferation of human myeloid progenitor cells. Interacting effects involving suppression, synergistic suppression, and blocking of suppression. J Immunol. 1993;150:3448–3458. - PubMed
-
- Calenda V, Chermann J C. HIV Tat protein potentiates in vitro granulomonocytic progenitor cell growth. Eur J Haematol. 1995;54:180–185. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

