Alpha and gamma interferons inhibit herpes simplex virus type 1 infection and spread in epidermal cells after axonal transmission
- PMID: 11689663
- PMCID: PMC114768
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.75.23.11821-11826.2001
Alpha and gamma interferons inhibit herpes simplex virus type 1 infection and spread in epidermal cells after axonal transmission
Abstract
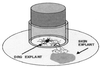
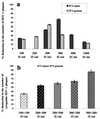
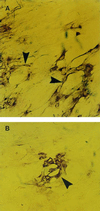
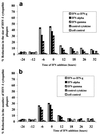
The ability of alpha interferon (IFN-alpha) and IFN-gamma to inhibit transmission of herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) from neuronal axon to epidermal cells (ECs), and subsequent spread in these cells was investigated in an in vitro dual-chamber model consisting of human fetal dorsal root ganglia (DRG) innervating autologous skin explants and compared with direct HSV-1 infection of epidermal explants. After axonal transmission from HSV-1-infected DRG neurons, both the number and size of viral cytopathic plaques in ECs was significantly reduced by addition of recombinant IFN-gamma and IFN-alpha to ECs in the outer chamber in a concentration-dependent fashion. Inhibition was maximal when IFNs were added at the same time as the DRG were infected with HSV-1. The mean numbers of plaques were reduced by 52% by IFN-alpha, 36% by IFN-gamma, and by 62% when IFN-alpha and IFN-gamma were combined, and the mean plaque size was reduced by 64, 43, and 72%, respectively. Similar but less-inhibitory effects of both IFNs were observed after direct infection of EC explants, being maximal when IFNs were added simultaneously or 6 h before HSV-1 infection. These results show that both IFN-alpha and IFN-gamma can interfere with HSV-1 infection after axonal transmission and subsequent spread of HSV-1 in ECs by a direct antiviral effect. Therefore, both IFN-alpha and -gamma could contribute to the control of HSV-1 spread and shedding in a similar fashion in recurrent herpetic lesions.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Neutralizing antibodies inhibit axonal spread of herpes simplex virus type 1 to epidermal cells in vitro.J Virol. 1999 Jul;73(7):5934-44. doi: 10.1128/JVI.73.7.5934-5944.1999. J Virol. 1999. PMID: 10364346 Free PMC article.
-
Beta interferon plus gamma interferon efficiently reduces acyclovir-resistant herpes simplex virus infection in mice in a T-cell-independent manner.J Gen Virol. 2010 Mar;91(Pt 3):591-8. doi: 10.1099/vir.0.016964-0. Epub 2009 Nov 11. J Gen Virol. 2010. PMID: 19906941
-
Macrophage control of herpes simplex virus type 1 replication in the peripheral nervous system.J Immunol. 1999 Mar 1;162(5):2895-905. J Immunol. 1999. PMID: 10072539
-
Infection and Transport of Herpes Simplex Virus Type 1 in Neurons: Role of the Cytoskeleton.Viruses. 2018 Feb 23;10(2):92. doi: 10.3390/v10020092. Viruses. 2018. PMID: 29473915 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Type I interferons and herpes simplex virus infection: a naked DNA approach as a therapeutic option?Immunol Res. 2001;24(1):1-11. doi: 10.1385/IR:24:1:01. Immunol Res. 2001. PMID: 11485206 Review.
Cited by
-
Why is eczema herpeticum unexpectedly rare?Antiviral Res. 2013 May;98(2):153-7. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2013.02.010. Epub 2013 Feb 22. Antiviral Res. 2013. PMID: 23439082 Free PMC article.
-
Herpes simplex virus (HSV)-specific T cells activated in the absence of IFN-gamma express alternative effector functions but are not protective against genital HSV-2 infection.J Reprod Immunol. 2010 Jan;84(1):8-15. doi: 10.1016/j.jri.2009.09.007. Epub 2009 Nov 25. J Reprod Immunol. 2010. PMID: 19942296 Free PMC article.
-
hMSCs treatment attenuates murine herpesvirus-68 (MHV-68) pneumonia through altering innate immune response via ROS/NLRP3 signaling pathway.Mol Biomed. 2023 Sep 14;4(1):27. doi: 10.1186/s43556-023-00137-z. Mol Biomed. 2023. PMID: 37704783 Free PMC article.
-
Bacterial artificial chromosome derived simian varicella virus is pathogenic in vivo.Virol J. 2013 Sep 8;10:278. doi: 10.1186/1743-422X-10-278. Virol J. 2013. PMID: 24010815 Free PMC article.
-
Two microRNAs encoded within the bovine herpesvirus 1 latency-related gene promote cell survival by interacting with RIG-I and stimulating NF-κB-dependent transcription and beta interferon signaling pathways.J Virol. 2012 Feb;86(3):1670-82. doi: 10.1128/JVI.06550-11. Epub 2011 Nov 30. J Virol. 2012. PMID: 22130548 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Balish M J, Abrams M E, Pumfery A M, Brandt C R. Enhanced inhibition of herpes simplex virus type 1 growth in human corneal fibroblasts by combinations of interferon-alpha and gamma. J Infect Dis. 1992;166:1401–1403. - PubMed
-
- Basham T Y, Nickoloff B J, Merigan T C, Morhenn V B. Recombinant gamma interferon differentially regulates class II antigen expression and biosynthesis on cultured normal human keratinocytes. J Interferon Res. 1985;5:23–32. - PubMed
-
- Bogdan C. The function of type I interferons in antimicrobial immunity. Curr Opin Immunol. 2000;4:419–424. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

