Repression of Ets-2-induced transactivation of the tau interferon promoter by Oct-4
- PMID: 11689681
- PMCID: PMC99954
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.21.23.7883-7891.2001
Repression of Ets-2-induced transactivation of the tau interferon promoter by Oct-4
Abstract
Oct-4 is a POU family transcription factor associated with potentially totipotent cells. Genes expressed in the trophectoderm but not in embryos prior to blastocyst formation may be targets for silencing by Oct-4. Here, we have tested this hypothesis with the tau interferon genes (IFNT genes), which are expressed exclusively in the trophectoderm of bovine embryos. IFNT promoters contain an Ets-2 enhancer, located at -79 to -70, and are up-regulated about 20-fold by the overexpression of Ets-2 in human JAr choriocarcinoma cells, which are permissive for IFNT expression. This enhancement was reversed in a dose-dependent manner by coexpression of Oct-4 but not either Oct-1 or Oct-2. When cells were transfected with truncated bovine IFNT promoters designed to eliminate potential octamer sites sequentially, luciferase reporter expression from each construct was still silenced by Oct-4. Full repression required both the N-terminal and POU domains of Oct-4, but neither domain used alone was an effective silencer. Oct-4 and Ets-2 formed a complex in vitro in the absence of DNA through binding of the POU domain of Oct-4 to a site located between the "pointed" and DNA binding domains of Ets-2. The two transcription factors were also coimmunoprecipitated after being expressed together in JAr cells. Oct-4, therefore, silences IFNT promoters by quenching Ets-2 transactivation. The POU domain most probably binds to Ets-2 directly, while the N-terminal domain inhibits transcription. These findings provide further evidence that the developmental switch to the trophectoderm is accompanied by the loss of Oct-4 silencing of key genes.
Figures
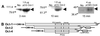
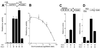






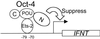
Similar articles
-
Regulation of interferon-tau (IFN-tau) gene promoters by growth factors that target the Ets-2 composite enhancer: a possible model for maternal control of IFN-tau production by the conceptus during early pregnancy.Endocrinology. 2004 Oct;145(10):4452-60. doi: 10.1210/en.2004-0606. Epub 2004 Jun 24. Endocrinology. 2004. PMID: 15217985
-
Control of interferon-tau gene expression by Ets-2.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998 Jul 7;95(14):7882-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.95.14.7882. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998. PMID: 9653109 Free PMC article.
-
The role of homeobox protein distal-less 3 and its interaction with ETS2 in regulating bovine interferon-tau gene expression-synergistic transcriptional activation with ETS2.Biol Reprod. 2008 Jul;79(1):115-24. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod.107.066647. Epub 2008 Mar 5. Biol Reprod. 2008. PMID: 18322277
-
POU domain factors in neural development.Adv Exp Med Biol. 1998;449:39-53. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-4871-3_4. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1998. PMID: 10026784 Review.
-
The virtuoso of versatility: POU proteins that flex to fit.J Mol Biol. 2000 Oct 6;302(5):1023-39. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.2000.4107. J Mol Biol. 2000. PMID: 11183772 Review.
Cited by
-
Functions of interferon tau as an immunological regulator for establishment of pregnancy.Reprod Med Biol. 2012 Jan 25;11(3):109-116. doi: 10.1007/s12522-011-0117-2. eCollection 2012 Jul. Reprod Med Biol. 2012. PMID: 29699116 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TF-Cluster: a pipeline for identifying functionally coordinated transcription factors via network decomposition of the shared coexpression connectivity matrix (SCCM).BMC Syst Biol. 2011 Apr 15;5:53. doi: 10.1186/1752-0509-5-53. BMC Syst Biol. 2011. PMID: 21496241 Free PMC article.
-
Generating pluripotent stem cells: differential epigenetic changes during cellular reprogramming.FEBS Lett. 2012 Aug 31;586(18):2874-81. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2012.07.024. Epub 2012 Jul 20. FEBS Lett. 2012. PMID: 22819821 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A mRNA landscape of bovine embryos after standard and MAPK-inhibited culture conditions: a comparative analysis.BMC Genomics. 2015 Apr 10;16(1):277. doi: 10.1186/s12864-015-1448-x. BMC Genomics. 2015. PMID: 25888366 Free PMC article.
-
Presence of Transcription Factor OCT4 Limits Interferon-tau Expression during the Pre-attachment Period in Sheep.Asian-Australas J Anim Sci. 2013 May;26(5):638-45. doi: 10.5713/ajas.2012.12462. Asian-Australas J Anim Sci. 2013. PMID: 25049833 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bazer F W, Spencer T E, Ott T L. Interferon tau: a novel pregnancy recognition signal. Am J Reprod Immunol. 1997;37:412–420. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
