Glycosylation defects and virulence phenotypes of Leishmania mexicana phosphomannomutase and dolicholphosphate-mannose synthase gene deletion mutants
- PMID: 11689705
- PMCID: PMC99981
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.21.23.8168-8183.2001
Glycosylation defects and virulence phenotypes of Leishmania mexicana phosphomannomutase and dolicholphosphate-mannose synthase gene deletion mutants
Abstract
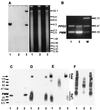
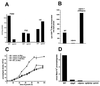
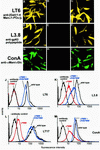
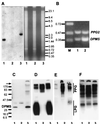
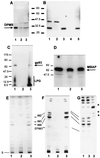
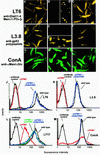
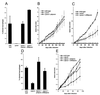
Leishmania parasites synthesize an abundance of mannose (Man)-containing glycoconjugates thought to be essential for virulence to the mammalian host and for viability. These glycoconjugates include lipophosphoglycan (LPG), proteophosphoglycans (PPGs), glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI)-anchored proteins, glycoinositolphospholipids (GIPLs), and N-glycans. A prerequisite for their biosynthesis is an ample supply of the Man donors GDP-Man and dolicholphosphate-Man. We have cloned from Leishmania mexicana the gene encoding the enzyme phosphomannomutase (PMM) and the previously described dolicholphosphate-Man synthase gene (DPMS) that are involved in Man activation. Surprisingly, gene deletion experiments resulted in viable parasite lines lacking the respective open reading frames (DeltaPMM and DeltaDPMS), a result against expectation and in contrast to the lethal phenotype observed in gene deletion experiments with fungi. L. mexicana DeltaDPMS exhibits a selective defect in LPG, protein GPI anchor, and GIPL biosynthesis, but despite the absence of these structures, which have been implicated in parasite virulence and viability, the mutant remains infectious to macrophages and mice. By contrast, L. mexicana DeltaPMM are largely devoid of all known Man-containing glycoconjugates and are unable to establish an infection in mouse macrophages or the living animal. Our results define Man activation leading to GDP-Man as a virulence pathway in Leishmania.
Figures


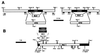

References
-
- Beverley S M, Turco S J. Lipophosphoglycan (LPG) and the identification of virulence genes in the protozoan parasite Leishmania. Trends Microbiol. 1998;6:35–40. - PubMed
-
- Boles E, Liebetrau W, Hofmann M, Zimmermann F K. A family of hexosephosphate mutases in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Eur J Biochem. 1994;220:83–96. - PubMed
-
- Brittingham A, Morrison C J, McMaster W R, McGwire B S, Chang K P, Mosser D M. Role of the Leishmania surface protease gp63 in complement fixation, cell adhesion, and resistance to complement-mediated lysis. J Immunol. 1995;15:3102–3111. - PubMed
-
- Collet J, Strooban V, Pirard M, Delpierre G, Van Schaftingen E. A new class of phosphotransferases phosphorylated on an aspartate residue in an amino-terminal DXDX(T/V) motif. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:14107–14112. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
