High-throughput variation detection and genotyping using microarrays
- PMID: 11691856
- PMCID: PMC311146
- DOI: 10.1101/gr.197201
High-throughput variation detection and genotyping using microarrays
Abstract
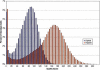
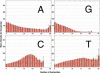
The genetic dissection of complex traits may ultimately require a large number of SNPs to be genotyped in multiple individuals who exhibit phenotypic variation in a trait of interest. Microarray technology can enable rapid genotyping of variation specific to study samples. To facilitate their use, we have developed an automated statistical method (ABACUS) to analyze microarray hybridization data and applied this method to Affymetrix Variation Detection Arrays (VDAs). ABACUS provides a quality score to individual genotypes, allowing investigators to focus their attention on sites that give accurate information. We have applied ABACUS to an experiment encompassing 32 autosomal and eight X-linked genomic regions, each consisting of approximately 50 kb of unique sequence spanning a 100-kb region, in 40 humans. At sufficiently high-quality scores, we are able to read approximately 80% of all sites. To assess the accuracy of SNP detection, 108 of 108 SNPs have been experimentally confirmed; an additional 371 SNPs have been confirmed electronically. To access the accuracy of diploid genotypes at segregating autosomal sites, we confirmed 1515 of 1515 homozygous calls, and 420 of 423 (99.29%) heterozygotes. In replicate experiments, consisting of independent amplification of identical samples followed by hybridization to distinct microarrays of the same design, genotyping is highly repeatable. In an autosomal replicate experiment, 813,295 of 813,295 genotypes are called identically (including 351 heterozygotes); at an X-linked locus in males (haploid), 841,236 of 841,236 sites are called identically.
Figures
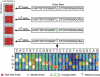
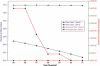
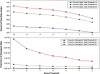
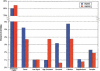

References
-
- Altshuler D, Pollara VJ, Cowles CR, Van Etten WJ, Baldwin J, Linton L, Lander ES. An SNP map of the human genome generated by reduced representation shotgun sequencing. Nature. 2000;407:513–516. - PubMed
-
- Cargill M, Altshuler D, Ireland J, Sklar P, Ardlie K, Patil N, Shaw N, Lane CR, Lim EP, Kalyanaraman N, et al. Characterization of single-nucleotide polymorphisms in coding regions of human genes. Nat Genet. 1999;22:231–238. - PubMed
-
- Chakravarti, A. Population genetics–making sense out of sequence. Nat. Genet. 21: 56–60. - PubMed
-
- Chee M, Yang R, Hubbell E, Berno A, Huang XC, Stern D, Winkler J, Lockhart DJ, Morris MS, Fodor SP. Accessing genetic information with high-density DNA arrays. Science. 1996;274:610–614. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
