GCP5 and GCP6: two new members of the human gamma-tubulin complex
- PMID: 11694571
- PMCID: PMC60259
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.12.11.3340
GCP5 and GCP6: two new members of the human gamma-tubulin complex
Abstract
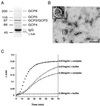
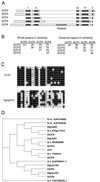
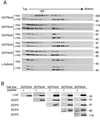
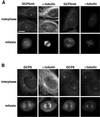
The gamma-tubulin complex is a large multiprotein complex that is required for microtubule nucleation at the centrosome. Here we report the purification and characterization of the human gamma-tubulin complex and the identification of its subunits. The human gamma-tubulin complex is a ring of ~25 nm, has a subunit structure similar to that reported for gamma-tubulin complexes from other species, and is able to nucleate microtubule polymerization in vitro. Mass spectrometry analysis of the human gamma-tubulin complex components confirmed the presence of four previously identified components (gamma-tubulin and gamma-tubulin complex proteins [GCPs] 2, 3, and 4) and led to the identification of two new components, GCP5 and GCP6. Sequence analysis revealed that the GCPs share five regions of sequence similarity and define a novel protein superfamily that is conserved in metazoans. GCP5 and GCP6, like other components of the gamma-tubulin complex, localize to the centrosome and associate with microtubules, suggesting that the entire gamma-tubulin complex takes part in both of these interactions. Stoichiometry experiments revealed that there is a single copy of GCP5 and multiple copies of gamma-tubulin, GCP2, GCP3, and GCP4 within the gamma-tubulin complex. Thus, the gamma-tubulin complex is conserved in structure and function, suggesting that the mechanism of microtubule nucleation is conserved.
Figures



References
-
- Burge C, Karlin S. Prediction of complete gene structures in human genomic DNA. J Mol Biol. 1997;268:78–94. - PubMed
-
- Detraves C, Mazarguil H, Lajoie MI, Julian M, Raynaud MB, Wright M. Protein complexes containing gamma-tubulin are present in mammalian brain microtubule protein preparations. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 1997;36:179–189. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

