In vivo role for actin-regulating kinases in endocytosis and yeast epsin phosphorylation
- PMID: 11694597
- PMCID: PMC60284
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.12.11.3668
In vivo role for actin-regulating kinases in endocytosis and yeast epsin phosphorylation
Abstract
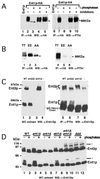
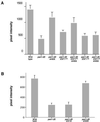
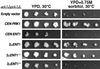
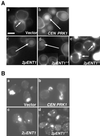
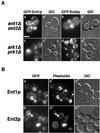
The yeast actin-regulating kinases Ark1p and Prk1p are signaling proteins localized to cortical actin patches, which may be sites of endocytosis. Interactions between the endocytic proteins Pan1p and End3p may be regulated by Prk1p-dependent threonine phosphorylation of Pan1p within the consensus sequence [L/I]xxQxTG. We identified two Prk1p phosphorylation sites within the Pan1p-binding protein Ent1p, a yeast epsin homologue, and demonstrate Prk1p-dependent phosphorylation of both threonines. Converting both threonines to either glutamate or alanine mimics constitutively phosphorylated or dephosphorylated Ent1p, respectively. Synthetic growth defects were observed in a pan1-20 ENT1(EE) double mutant, suggesting that Ent1p phosphorylation negatively regulates the formation/activity of a Pan1p-Ent1p complex. Interestingly, pan1-20 ent2 Delta but not pan1-20 ent1 Delta double mutants had improved growth and endocytosis over the pan1-20 mutant. We found that actin-regulating Ser/Thr kinase (ARK) mutants exhibit endocytic defects and that overexpressing either wild-type or alanine-substituted Ent1p partially suppressed phenotypes associated with loss of ARK kinases, including growth, endocytosis, and actin localization defects. Consistent with synthetic growth defects of pan1-20 ENT1(EE) cells, overexpressing glutamate-substituted Ent1p was deleterious to ARK mutants. Surprisingly, overexpressing the related Ent2p protein could not suppress ARK kinase mutant phenotypes. These results suggest that Ent1p and Ent2p are not completely redundant and may perform opposing functions in endocytosis. These data support the model that, as for clathrin-dependent recycling of synaptic vesicles, yeast endocytic protein phosphorylation inhibits endocytic functions.
Figures
References
-
- Ayscough KR. Endocytosis and the development of cell polarity in yeast require a dynamic F-actin cytoskeleton. Curr Biol. 2000;10:1587–1590. - PubMed
-
- Benmerah A, Poupon V, Cerf-Bensussan N, Dautry-Varsat A. Mapping of Eps15 domains involved in its targeting to clathrin-coated pits. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:3288–3295. - PubMed
-
- Carbone R, Fre S, Iannolo G, Belleudi F, Mancini P, Pelicci PG, Torrisi MR, Di Fiore PP. eps15 and eps15R are essential components of the endocytic pathway. Cancer Res. 1997;57:5498–5504. - PubMed
-
- Chen H, Fre S, Slepnev VI, Capua MR, Takei K, Butler MH, Di Fiore PP, De Camilli P. Epsin is an EH-domain-binding protein implicated in clathrin-mediated endocytosis. Nature. 1998;394:793–797. - PubMed
-
- Chen H, Slepnev VI, Di Fiore PP, De Camilli P. The interaction of epsin and Eps15 with the clathrin adaptor AP-2 is inhibited by mitotic phosphorylation and enhanced by stimulation-dependent dephosphorylation in nerve terminals. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:3257–3260. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

