Beta1 integrins show specific association with CD98 protein in low density membranes
- PMID: 11696247
- PMCID: PMC59658
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2091-2-10
Beta1 integrins show specific association with CD98 protein in low density membranes
Abstract
Background: The CD98 (4F2, FRP-1) is a widely expressed cell surface protein heterodimer composed of a glycosylated heavy chain and a non-glycosylated light chain. Originally described as a T cell activation antigen, it was later shown to function in amino acid transport, cell fusion and homotypic cell aggregation. Several lines of evidence suggest its functional interaction with integrins but the biochemical basis for this interaction has been unclear.
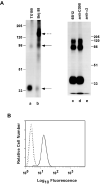
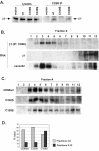
Results: We demonstrate that CD98 constitutively and specifically associates with beta1 integrins (alpha2beta1,alpha3beta1, alpha5beta1 and alpha6beta1), but minimally with alpha4beta1. Integrin-CD98 association was established by reciprocal immunoprecipitation experiments, and confirmed by CD98-induced clustering of alpha3beta1 but not alpha4beta1 on the surface of rhabdomyosarcoma cells. Integrin-CD98 association is independent of the alpha subunit cytoplasmic tail, is maintained in alpha3beta1 ligand-interaction deficient mutants, and is not inhibited by EDTA. Within the CD98 heavy chain, a C109S mutation (but not a C330S mutation) caused a loss of beta1 integrin association. The same C109S mutation also caused a loss of CD98 light chain association. Importantly, CD98 associated selectively with beta1 integrins present in low density "light membrane" fractions on a sucrose gradient. CD98 was not present in dense fractions that contained the majority of beta1 integrins. Notably, the C109S mutant of CD98, that did not associate with beta1 integrins, showed also a reduced localization into light membrane fractions.
Conclusions: We demonstrate that CD98 association with beta1 integrins is specific, occurs in the context of low density membranes, and may require the CD98 light chain.
Figures

Similar articles
-
CD98 activation increases surface expression and clusteringof beta1 integrins in MCF-7 cells through FAK/Src- and cytoskeleton-independent mechanisms.Exp Mol Med. 2008 Jun 30;40(3):261-70. doi: 10.3858/emm.2008.40.3.261. Exp Mol Med. 2008. PMID: 18587263 Free PMC article.
-
Physical association and functional interaction between beta1 integrin and CD98 on human T lymphocytes.Mol Immunol. 2003 Jan;39(12):739-51. doi: 10.1016/s0161-5890(02)00255-9. Mol Immunol. 2003. PMID: 12531285
-
CD98-mediated links between amino acid transport and beta 1 integrin distribution in polarized columnar epithelia.J Biol Chem. 2001 Oct 19;276(42):39282-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M105077200. Epub 2001 Aug 15. J Biol Chem. 2001. PMID: 11507094
-
CD98 signals controlling tumorigenesis.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2016 Dec;81(Pt A):148-150. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2016.11.005. Epub 2016 Nov 10. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2016. PMID: 27840151 Review.
-
Function of fusion regulatory proteins (FRPs) in immune cells and virus-infected cells.Crit Rev Immunol. 2000;20(3):167-96. Crit Rev Immunol. 2000. PMID: 10968370 Review.
Cited by
-
CD98 activation increases surface expression and clusteringof beta1 integrins in MCF-7 cells through FAK/Src- and cytoskeleton-independent mechanisms.Exp Mol Med. 2008 Jun 30;40(3):261-70. doi: 10.3858/emm.2008.40.3.261. Exp Mol Med. 2008. PMID: 18587263 Free PMC article.
-
Heteromeric Solute Carriers: Function, Structure, Pathology and Pharmacology.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021;21:13-127. doi: 10.1007/5584_2020_584. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021. PMID: 33052588 Review.
-
Molecular mapping of transmembrane mechanotransduction through the β1 integrin-CD98hc-TRPV4 axis.J Cell Sci. 2020 Nov 2;133(20):jcs248823. doi: 10.1242/jcs.248823. J Cell Sci. 2020. PMID: 32989042 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolic activation-related CD147-CD98 complex.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2005 Aug;4(8):1061-71. doi: 10.1074/mcp.M400207-MCP200. Epub 2005 May 18. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2005. PMID: 15901826 Free PMC article.
-
Overexpression of CD98 in intestinal epithelium dysregulates miRNAs and their targeted proteins along the ileal villus-crypt axis.Sci Rep. 2018 Nov 1;8(1):16220. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-34474-9. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 30385787 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Haynes BF, Hemler ME, Mann DL, Eisenbarth GS, Shelhamer J, Mostowski HS, et al. Characterization of a monoclonal antibody (4F2) that binds to human monocytes and to a subset of activated lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1981;126:1409–1414. - PubMed
-
- Tabata N, Ito M, Shimokata K, Suga S, Ohgimoto S, Tsurudome M, et al. Expression of fusion regulatory proteins (FRPs) on human peripheral blood monocytes. J Immunol. 1994;153:3256. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

