Intestinal mast cell progenitors require CD49dbeta7 (alpha4beta7 integrin) for tissue-specific homing
- PMID: 11696590
- PMCID: PMC2195984
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.194.9.1243
Intestinal mast cell progenitors require CD49dbeta7 (alpha4beta7 integrin) for tissue-specific homing
Abstract
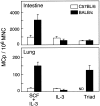
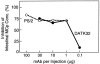
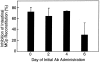
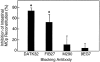
Mast cells (MCs) are centrally important in allergic inflammation of the airways, as well as in the intestinal immune response to helminth infection. A single lineage of bone marrow (BM)-derived progenitors emigrates from the circulation and matures into phenotypically distinct MCs in different tissues. Because the mechanisms of MC progenitor (MCp) homing to peripheral tissues have not been evaluated, we used limiting dilution analysis to measure the concentration of MCp in various tissues of mice deficient for candidate homing molecules. MCp were almost completely absent in the small intestine but were present in the lung, spleen, BM, and large intestine of beta7 integrin-deficient mice (on the C57BL/6 background), indicating that a beta7 integrin is critical for homing of these cells to the small intestine. MCp concentrations were not altered in the tissues of mice deficient in the alphaE integrin (CD103), the beta2 integrin (CD18), or the recombination activating gene (RAG)-2 gene either alone or in combination with the interleukin (IL)-receptor common gamma chain. Therefore, it is the alpha4beta7 integrin and not the alphaEbeta7 integrin that is critical, and lymphocytes and natural killer cells play no role in directing MCp migration under basal conditions. When MCp in BALB/c mice were eliminated with sublethal doses of gamma-radiation and then reconstituted with syngeneic BM, the administration of anti-alpha4beta7 integrin, anti-alpha4 integrin, anti-beta7 integrin, or anti-MAdCAM-1 monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) blocked the recovery of MCp in the small intestine. The blocking mAbs could be administered as late as 4 d after BM reconstitution with optimal inhibition, implying that the MCp must arise first in the BM, circulate in the vasculature, and then translocate into the intestine. Inasmuch as MCp are preserved in the lungs of beta7 integrin-deficient and anti-alpha4beta7 integrin-treated mice but not in the small intestine, alpha4beta7 integrin is critical for tissue specific extravasation for localization of MCp in the small intestine, but not the lungs.
Figures
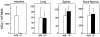



Similar articles
-
Constitutive homing of mast cell progenitors to the intestine depends on autologous expression of the chemokine receptor CXCR2.Blood. 2005 Jun 1;105(11):4308-13. doi: 10.1182/blood-2004-09-3578. Epub 2005 Feb 10. Blood. 2005. PMID: 15705791 Free PMC article.
-
β7 Integrin controls mast cell recruitment, whereas αE integrin modulates the number and function of CD8+ T cells in immune complex-mediated tissue injury.J Immunol. 2014 May 1;192(9):4112-21. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1300926. Epub 2014 Mar 26. J Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24670804
-
Alpha-4 integrins and VCAM-1, but not MAdCAM-1, are essential for recruitment of mast cell progenitors to the inflamed lung.Blood. 2006 Sep 1;108(5):1588-94. doi: 10.1182/blood-2005-12-012781. Epub 2006 May 2. Blood. 2006. PMID: 16670268 Free PMC article.
-
Role of beta7 integrins in intestinal lymphocyte homing and retention.Curr Mol Med. 2009 Sep;9(7):836-50. doi: 10.2174/156652409789105525. Curr Mol Med. 2009. PMID: 19860663 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mast cells: ontogeny, homing, and recruitment of a unique innate effector cell.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2006 Jun;117(6):1285-91. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2006.04.017. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2006. PMID: 16750988 Review.
Cited by
-
The interplay between mast cells, pineal gland, and circadian rhythm: Links between histamine, melatonin, and inflammatory mediators.J Pineal Res. 2021 Mar;70(2):e12699. doi: 10.1111/jpi.12699. Epub 2020 Nov 29. J Pineal Res. 2021. PMID: 33020940 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mast cell ontogeny: From fetal development to life-long health and disease.Immunol Rev. 2023 May;315(1):31-53. doi: 10.1111/imr.13191. Epub 2023 Feb 8. Immunol Rev. 2023. PMID: 36752151 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mast Cell-Dependent CD8+ T-cell Recruitment Mediates Immune Surveillance of Intestinal Tumors in ApcMin/+ Mice.Cancer Immunol Res. 2018 Mar;6(3):332-347. doi: 10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-17-0424. Epub 2018 Jan 30. Cancer Immunol Res. 2018. PMID: 29382671 Free PMC article.
-
The role of integrins in the pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease: Approved and investigational anti-integrin therapies.Med Res Rev. 2020 Jan;40(1):245-262. doi: 10.1002/med.21601. Epub 2019 Jun 19. Med Res Rev. 2020. PMID: 31215680 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ikaros limits basophil development by suppressing C/EBP-α expression.Blood. 2013 Oct 10;122(15):2572-81. doi: 10.1182/blood-2013-04-494625. Epub 2013 Aug 29. Blood. 2013. PMID: 23990620 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Williams, C.M., and S.J. Galli. 2000. The diverse potential effector and immunoregulatory roles of mast cells in allergic disease. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 105:847–859. - PubMed
-
- Metcalfe, D.D., D. Baram, and Y.A. Mekori. 1997. Mast cells. Physiol. Rev. 77:1033–1079. - PubMed
-
- Gurish, M.F., W.S. Pear, R.L. Stevens, M.L. Scott, K. Sokol, N. Ghildyal, M.J. Webster, X. Hu, K.F. Austen, D. Baltimore, and D.S. Friend. 1995. Tissue-regulated differentiation and maturation of a v-abl-immortalized mast cell-committed progenitor. Immunity. 3:1–20. - PubMed
-
- Friend, D.S., N. Ghildyal, K.F. Austen, M.F. Gurish, R. Matsumoto, and R.L. Stevens. 1996. Mast cells that reside at different locations in the jejunum of mice infected with Trichinella spiralis exhibit sequential changes in their granule ultrastructure and chymase phenotype. J. Cell Biol. 135:279–290. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Malaviya, R., T. Ikeda, E. Ross, and S.N. Abraham. 1996. Mast cell modulation of neutrophil influx and bacterial clearance at sites of infection through TNF-alpha. Nature. 381:77–80. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

