Subcellular and subsynaptic localization of presynaptic and postsynaptic kainate receptor subunits in the monkey striatum
- PMID: 11698586
- PMCID: PMC6762275
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.21-22-08746.2001
Subcellular and subsynaptic localization of presynaptic and postsynaptic kainate receptor subunits in the monkey striatum
Abstract
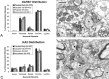
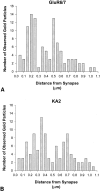
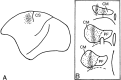
The localization and functions of kainate receptors (KARs) in the CNS are still poorly known. In the striatum, GluR6/7 and KA2 immunoreactivity is expressed presynaptically in a subpopulation of glutamatergic terminals and postsynaptically in dendrites and spines. The goal of this study was to further characterize the subcellular and subsynaptic localization of kainate receptor subunits in the monkey striatum. Immunoperoxidase data reveal that the relative abundance of GluR6/7- and KA2-immunoreactive terminals is homogeneous throughout the striatum irrespective of the differential degree of striatal degeneration in Huntington's disease. Pre-embedding and post-embedding immunogold data indicate that >70% of the presynaptic or postsynaptic GluR6/7 and KA2 labeling is expressed intracellularly. In material stained with the post-embedding immunogold method, approximately one-third of plasma membrane-bound gold particles labeling in axon terminals and spines is associated with asymmetric synapses, thereby representing synaptic kainate receptor subunits. On the other hand, >60% of the plasma-membrane bound labeling is extrasynaptic. Both GluR6/7 and KA2 labeling in glutamatergic terminals often occurs in clusters of gold particles along the membrane of large vesicular organelles located at various distances from the presynaptic grid. Anterograde labeling from the primary motor cortex or the centromedian thalamic nucleus indicate that both corticostriatal and thalamostriatal terminals express presynaptic GluR6/7 and KA2 immunoreactivity in the postcommissural putamen. In conclusion, these data demonstrate that kainate receptors in the striatum display a pattern of subcellular distribution different from other ionotropic glutamate receptor subtypes, but consistent with their metabotropic-like functions recently shown in the hippocampus.
Figures






References
-
- Anwyl R. Metabotropic glutamate receptors: electrophysiological properties and role in plasticity. Brain Res Rev. 1999;29:83–120. - PubMed
-
- Aronin N, Chase K, Young C, Sapp E, Schwarz C, Matta N, Kornreich R, Landwehrmeyer B, Bird E, Beal MF, Vonsattel JP, Smith T, Carraway R, Boyce FM, Young AB, Penney JB, DiFiglia M. CAG expansion affects the expression of mutant huntingtin in the Huntington's disease brain. Neuron. 1995;15:1193–1201. - PubMed
-
- Baude A, Nusser Z, Roberts JD, Mulvihill E, McIlhinney RAJ, Somogyi P. The metabotropic glutamate receptor (mGluR1a) is concentrated at perisynaptic membrane of neuronal subpopulations as detected by immunogold reaction. Neuron. 1993;11:771–787. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
