Stimulation of endothelin B receptors in astrocytes induces cAMP response element-binding protein phosphorylation and c-fos expression via multiple mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathways
- PMID: 11698596
- PMCID: PMC6762276
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.21-22-08842.2001
Stimulation of endothelin B receptors in astrocytes induces cAMP response element-binding protein phosphorylation and c-fos expression via multiple mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathways
Abstract
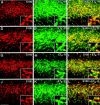
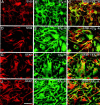
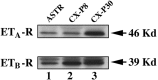
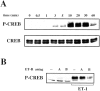
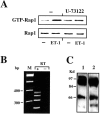
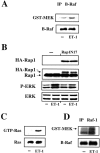
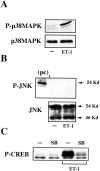
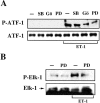
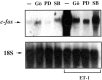
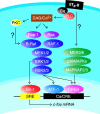
The vasoconstrictor peptide endothelin (ET-1) exerts its physiological and pathological effects via activation of ET(A) and ET(B) receptor (ET-R) subtypes. In this study, we demonstrate that both ET-R subtypes are highly expressed in rat astrocytes in vivo, indicating that these cells are potential targets of the biological effects of ET-1 in the brain. In cultured cortical astrocytes, both ET-R subtypes are expressed, and selective stimulation of ET(B)-R with ET-1 induces phosphorylation of cAMP response element-binding protein (CREB). The signal transduction pathway activated by ET-1 includes the Rap1/B-Raf and the Ras/Raf-1 complexes, protein kinase C (PKC) together with extracellular signal-regulated kinases (ERK), and the ribosomal S6 kinase (RSK) isoforms RSK2 and RSK3, two kinases that lie immediately downstream of ERK and are able to phosphorylate CREB. Moreover, ET-1 activates the p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK)-dependent, but not the c-jun N-terminal kinase (JNK)-dependent pathway. By using selective protein kinase inhibitors and expression of dominant-negative Rap1 protein, we also found that the Rap1/PKC/ERK-dependent pathway induces the phosphorylation of activating transcription factor-1, CREB, and Elk-1, whereas the p38MAPK-dependent pathway only causes CREB phosphorylation. ET-1-induced transcription of the immediate early gene c-fos requires the concomitant activation of both the PKC/ERK- and p38MAPK-dependent pathways, because inhibitors of either pathway block the ET-1-induced increase of c-fos mRNA. Our findings indicate that changes in the expression of cAMP response element-dependent immediate and delayed response genes could play a pivotal role in the physiological effects elicited by ET-1 in astrocytes.
Figures

References
-
- Barnier JV, Papin C, Eychene A, Lecoq O, Calothy G. The mouse B-raf gene encodes multiple protein isoforms with tissue-specific expression. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:23381–23389. - PubMed
-
- Böhm M, Moellmann G, Cheng E, Alvarez-Franco M, Wagner S, Sassone-Corsi P, Halaban R. Identification of p90RSK as the probable CREB-Ser133 kinase in human melanocytes. Cell Growth Differ. 1995;6:291–302. - PubMed
-
- Campbell SL, Khosravi-Far R, Rossman KL, Clark GJ, Der CJ. Increasing complexity of Ras signaling. Oncogene. 1998;17:1395–1413. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
