Multipotent stem cells from the mouse basal forebrain contribute GABAergic neurons and oligodendrocytes to the cerebral cortex during embryogenesis
- PMID: 11698597
- PMCID: PMC6762260
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.21-22-08854.2001
Multipotent stem cells from the mouse basal forebrain contribute GABAergic neurons and oligodendrocytes to the cerebral cortex during embryogenesis
Abstract
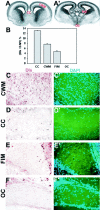
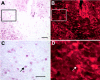
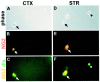
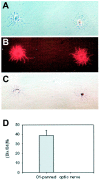
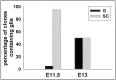
During CNS development, cell migrations play an important role, adding to the cellular complexity of different regions. Earlier studies have shown a robust migration of cells from basal forebrain into the overlying dorsal forebrain during the embryonic period. These immigrant cells include GABAergic neurons that populate the cerebral cortex and hippocampus. In this study we have examined the fate of other basal forebrain cells that migrate into the dorsal forebrain, identifying basal cells using an antibody that recognizes both early (dlx1/2) and late (dlx 5/6) members of the dlx homeobox gene family. We found that a subpopulation of cortical and hippocampal oligodendrocytes are also ventral-derived. We traced the origin of these cells to basal multipotent stem cells capable of generating both GABAergic neurons and oligodendrocytes. A clonal analysis showed that basal forebrain stem cells produce significantly more GABAergic neurons than dorsal forebrain stem cells from the same embryonic age. Moreover, stem cell clones from basal forebrain are significantly more likely to contain both GABAergic neurons and oligodendrocytes than those from dorsal. This indicates that forebrain stem cells are regionally specified. Whereas dlx expression was not detected within basal stem cells growing in culture, these cells produced dlx-positive products that are capable of migration. These data indicate that the developing cerebral cortex incorporates both neuronal and glial products of basal forebrain and suggest that these immigrant cells arise from a common progenitor, a dlx-negative basal forebrain stem cell.
Figures

References
-
- Akiyama Y, Honmou O, Kato T, Uede T, Hashi K, Kocsis JD. Transplantation of clonal neural precursor cells derived from adult human brain establishes functional peripheral myelin in the rat spinal cord. Exp Neurol. 2001;167:27–39. - PubMed
-
- Anderson SA, Eisenstat DD, Shi L, Rubenstein JL. Interneuron migration from basal forebrain to neocortex: dependence on Dlx genes. Science. 1997;278:474–476. - PubMed
-
- Anderson SA, Marin O, Horn C, Jennings K, Rubenstein JL. Distinct cortical migrations from the medial and lateral ganglionic eminences. Development. 2001;128:353–363. - PubMed
-
- Barres BA, Koroshetz WJ, Swartz KJ, Chun LL, Corey DP. Ion channel expression by white matter glia: the O-2A glial progenitor cell. Neuron. 1990;4:507–524. - PubMed
-
- Betarbet R, Zigova T, Bakay RA, Luskin MB. Dopaminergic and GABAergic interneurons of the olfactory bulb are derived from the neonatal subventricular zone. Int J Dev Neurosci. 1996;14:921–930. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
