P2 receptor-types involved in astrogliosis in vivo
- PMID: 11704637
- PMCID: PMC1573045
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0704353
P2 receptor-types involved in astrogliosis in vivo
Abstract
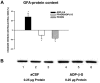
1. In the nucleus accumbens (NAc) of rats, the involvement of P2X and P2Y receptors in the generation of astrogliosis in vivo, was investigated by local application of their respective ligands. The agonists used had selectivities for P2X1,3 (alpha,beta-methylene adenosine 5'-triphosphate; alpha,beta-meATP), P2Y1,12 (adenosine 5'-O-(2-thiodiphosphate; ADP-beta-S) and P2Y2,4,6 receptors (uridine 5'-O-(3-thiotriphosphate; UTP-gamma-S). Pyridoxalphosphate-6-azophenyl-2,4-disulphonic acid (PPADS) was used as a non-selective antagonist. The astroglial reaction was studied by means of immunocytochemical double-labelling with antibodies to glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) and 5-bromo-2'-deoxyuridine (BrdU). 2. The agonist-induced changes in comparison to the artificial cerebrospinal fluid (aCSF)-treated control side reveal a strong mitogenic potency of ADP-beta-S and alpha,beta-meATP, whereas UTP-gamma-S was ineffective. The P2 receptor antagonist PPADS decreased the injury-induced proliferation when given alone and in addition inhibited all agonist effects. 3. The observed morphogenic changes included hypertrophy of astrocytes, elongation of astrocytic processes and up-regulation of GFAP. A significant increase of both GFAP-immunoreactivity (IR) and GFA-protein content (by using Western blotting) was found after microinfusion of alpha,beta-meATP or ADP-beta-S. In contrast, UTP-gamma-S failed to increase the GFAP-IR. The morphogenic effects were also inhibited by pre-treatment with PPADS. 4. A double immunofluorescence approach with confocal laser scanning microscopy showed the localisation of P2X3 and P2Y1 receptors on the GFAP-labelled astrocytes. 5. In conclusion, the data suggest that P2Y (P2Y1 or P2Y12) receptor subtypes are involved in the generation of astrogliosis in the NAc of rats, with a possible minor contribution of P2X receptor subtypes.
Figures





Similar articles
-
P2Y receptor expression on astrocytes in the nucleus accumbens of rats.Neuroscience. 2004;127(2):431-41. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2004.05.003. Neuroscience. 2004. PMID: 15262333
-
P2 receptor-mediated stimulation of the PI3-K/Akt-pathway in vivo.Glia. 2009 Aug 1;57(10):1031-45. doi: 10.1002/glia.20827. Glia. 2009. PMID: 19115395
-
P2 receptor-mediated proliferative effects on astrocytes in vivo.Glia. 1999 Dec;28(3):190-200. Glia. 1999. PMID: 10559778
-
Enhanced P2Y1 receptor expression in the brain after sensitisation with d-amphetamine.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2003 May;167(2):187-94. doi: 10.1007/s00213-002-1386-6. Epub 2003 Mar 22. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2003. PMID: 12652343
-
Comparison of P2 receptor subtypes producing dilation in rat intracerebral arterioles.Stroke. 2003 Jun;34(6):1473-8. doi: 10.1161/01.STR.0000071527.10129.65. Epub 2003 May 1. Stroke. 2003. PMID: 12730558
Cited by
-
Nucleotide signaling in nervous system development.Pflugers Arch. 2006 Aug;452(5):573-88. doi: 10.1007/s00424-006-0067-4. Epub 2006 Apr 25. Pflugers Arch. 2006. PMID: 16639549 Review.
-
Involvement of Enteric Glia in Small Intestine Neuromuscular Dysfunction of Toll-Like Receptor 4-Deficient Mice.Cells. 2020 Mar 31;9(4):838. doi: 10.3390/cells9040838. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32244316 Free PMC article.
-
P2Y2 receptor expression is altered in rats after spinal cord injury.Int J Dev Neurosci. 2010 Oct;28(6):413-21. doi: 10.1016/j.ijdevneu.2010.07.001. Epub 2010 Jul 7. Int J Dev Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 20619335 Free PMC article.
-
Differential modulation of ATP-induced calcium signalling by A1 and A2 adenosine receptors in cultured cortical astrocytes.Br J Pharmacol. 2004 Mar;141(6):935-42. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0705707. Epub 2004 Mar 1. Br J Pharmacol. 2004. PMID: 14993103 Free PMC article.
-
2-Substitution of adenine nucleotide analogues containing a bicyclo[3.1.0]hexane ring system locked in a northern conformation: enhanced potency as P2Y1 receptor antagonists.J Med Chem. 2003 Nov 6;46(23):4974-87. doi: 10.1021/jm030127+. J Med Chem. 2003. PMID: 14584948 Free PMC article.
References
-
- ABBRACCHIO M.P., BURNSTOCK G. Purinoceptors: are there families of P2X and P2Y purinoceptors. Pharmac. Ther. 1994;64:445–475. - PubMed
-
- ABBRACCHIO M.P., BRAMBILLA R., CERUTI S., CATTABENI F. Signalling mechanisms involved in P2Y receptor-mediated reactive astrogliosis. Progr. Brain Res. 1999;120:333–342. - PubMed
-
- ABBRACCHIO M.P., CERUTI S., BOLEGO C., PUGLISI L., BURNSTOCK G., CATTABENI F.Trophic roles of P2 purinoceptors in central nervous system astroglial cells P2 Purinoceptors: Localisation, Function and Transduction Mechanisms 1996Chichester: John Wiley & Sons; 142–147.ed. Chadwick, D.J. & Goode, J.A., Ciba Foundation Symposium 198 - PubMed
-
- ABBRACCHIO M.P., CERUTI S., LANGFELDER R., CATTABENI F., SAFFREY M.J., BURNSTOCK G. Effects of ATP analogues and basic fibroblast growth factor on astroglial cell differentiation in primary cultures of rat striatum. Int. J. Dev. Neurosci. 1995;13:685–693. - PubMed
-
- ABBRACCHIO M.P., SAFFREY M.J., HÖPKER V., BURNSTOCK G. Modulation of astroglial cell proliferation by analogues of adenosine and ATP in primary cultures of rat striatum. Neuroscience. 1994;59:67–76. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

