Chronic morphine induces up-regulation of the pro-apoptotic Fas receptor and down-regulation of the anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 oncoprotein in rat brain
- PMID: 11704646
- PMCID: PMC1573055
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0704364
Chronic morphine induces up-regulation of the pro-apoptotic Fas receptor and down-regulation of the anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 oncoprotein in rat brain
Abstract
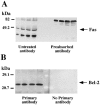
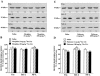
1. This study was designed to assess the influence of activation and blockade of the endogenous opioid system in the brain on two key proteins involved in the regulation of programmed cell death: the pro-apoptotic Fas receptor and the anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 oncoprotein. 2. The acute treatment of rats with the mu-opioid receptor agonist morphine (3-30 mg x kg(-1), i.p., 2 h) did not modify the immunodensity of Fas or Bcl-2 proteins in the cerebral cortex. Similarly, the acute treatment with low and high doses of the antagonist naloxone (1 and 100 mg x kg(-1), i.p., 2 h) did not alter Fas or Bcl-2 protein expression in brain cortex. These results discounted a tonic regulation through opioid receptors on Fas and Bcl-2 proteins in rat brain. 3. Chronic morphine (10-100 mg x kg(-1), 5 days, and 10 mg x kg(-1), 13 days) induced marked increases (47-123%) in the immunodensity of Fas receptor in the cerebral cortex. In contrast, chronic morphine (5 and 13 days) decreased the immunodensity of Bcl-2 protein (15-30%) in brain cortex. Chronic naloxone (10 mg x kg(-1), 13 days) did not alter the immunodensities of Fas and Bcl-2 proteins in the cerebral cortex. 4. The concurrent chronic treatment (13 days) of naloxone (10 mg x kg(-1)) and morphine (10 mg x kg(-1)) completely prevented the morphine-induced increase in Fas receptor and decrease in Bcl-2 protein immunoreactivities in the cerebral cortex. 5. The results indicate that morphine, through the sustained activation of opioid receptors, can promote abnormal programmed cell death by enhancing the expression of pro-apoptotic Fas receptor protein and damping the expression of anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 oncoprotein.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Effects of opiate drugs on Fas-associated protein with death domain (FADD) and effector caspases in the rat brain: regulation by the ERK1/2 MAP kinase pathway.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2007 Feb;32(2):399-411. doi: 10.1038/sj.npp.1301040. Epub 2006 Feb 8. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2007. PMID: 16482086
-
Acute and chronic effects of morphine and naloxone on the phosphorylation of neurofilament-H proteins in the rat brain.Neurosci Lett. 2001 May 18;304(1-2):37-40. doi: 10.1016/s0304-3940(01)01729-3. Neurosci Lett. 2001. PMID: 11335049
-
Attenuation of tolerance to opioid-induced antinociception and protection against morphine-induced decrease of neurofilament proteins by idazoxan and other I2-imidazoline ligands.Br J Pharmacol. 1998 Sep;125(1):175-85. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0702031. Br J Pharmacol. 1998. PMID: 9776358 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of Fas receptor proteins and dynamin during opiate addiction and induction of opiate withdrawal in rat brain.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2003 Nov;368(5):421-31. doi: 10.1007/s00210-003-0801-9. Epub 2003 Oct 3. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2003. PMID: 14530904
-
[Apoptosis--molecular basis in pathogenesis of selected chronic inflammatory and neoplastic diseases].Pol Merkur Lekarski. 2005 Mar;18(105):329-31. Pol Merkur Lekarski. 2005. PMID: 15997645 Review. Polish.
Cited by
-
Glutamate-induced apoptosis in primary cortical neurons is inhibited by equine estrogens via down-regulation of caspase-3 and prevention of mitochondrial cytochrome c release.BMC Neurosci. 2005 Feb 24;6:13. doi: 10.1186/1471-2202-6-13. BMC Neurosci. 2005. PMID: 15730564 Free PMC article.
-
Methadone-induced Damage to White Matter Integrity in Methadone Maintenance Patients: A Longitudinal Self-control DTI Study.Sci Rep. 2016 Jan 22;6:19662. doi: 10.1038/srep19662. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 26794650 Free PMC article.
-
Role of phosphodiesterase inhibitor Ibudilast in morphine-induced hippocampal injury.J Inj Violence Res. 2014 Jul;6(2):72-8. doi: 10.5249/jivr.v6i2.497. Epub 2013 Oct 11. J Inj Violence Res. 2014. PMID: 24121451 Free PMC article.
-
Metformin prevents morphine-induced apoptosis in rats with diabetic neuropathy: a possible mechanism for attenuating morphine tolerance.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2022 Nov;395(11):1449-1462. doi: 10.1007/s00210-022-02283-7. Epub 2022 Sep 2. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36050544
-
Chronic methadone treatment and repeated withdrawal impair cognition and increase the expression of apoptosis-related proteins in mouse brain.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2007 Jul;193(1):107-20. doi: 10.1007/s00213-007-0751-x. Epub 2007 Mar 24. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2007. PMID: 17384938
References
-
- ABBRACCHIO M.P., ONGINI E., MEMO M. Disclosing apoptosis in the CNS. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 1999;20:129–131. - PubMed
-
- ADAMS J.M., CORY S. The Bcl-2 protein family: arbiters of cell survival. Science. 1998;281:1322–1326. - PubMed
-
- DAWSON G., DAWSON S.A., GOSWAMI R. Chronic exposure to κ-opioids enhances the susceptibility of immortalized neurons (F-11 k7) to apoptosis-inducing drugs by a mechanism that may involve ceramide. J. Neurochem. 1997;68:2363–2370. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

