Bacterial fimbriae and their peptides activate human gingival epithelial cells through Toll-like receptor 2
- PMID: 11705912
- PMCID: PMC98826
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.69.12.7387-7395.2001
Bacterial fimbriae and their peptides activate human gingival epithelial cells through Toll-like receptor 2
Abstract
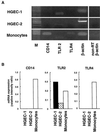
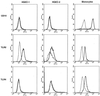
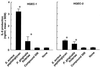
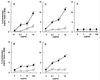
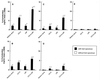
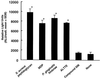
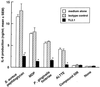
Gingival epithelial cells are a central component of the barrier between oral microflora and internal tissues. Host responses to periodontopathic bacteria and surface components containing fimbriae are thought to be important in the development and progression of periodontal diseases. To elucidate this mechanism, we established immortalized human gingival epithelial cells (HGEC) that were transfected with human papillomavirus. HGEC predominantly expressed Toll-like receptor (TLR) 2, but not TLR4 or CD14. They also induced interleukin-8 (IL-8) production when stimulated with Porphyromonas gingivalis fimbriae and Staphylococcus aureus peptidoglycan, but not Escherichia coli-type synthetic lipid A. Furthermore, an active synthetic peptide composed of residues 69 to 73 (ALTTE) of the fimbrial subunit protein, derived from P. gingivalis and similar to a common component of cell wall peptidoglycans in parasitic bacteria, N-acetylmuramyl-L-alanyl-D-isoglutamine (MDP), significantly induced IL-8 production and NF-kappaB activation in HGEC, and these cytokine-producing activities were augmented by a complex of soluble CD14 and lipopolysaccharide-binding protein (LBP). IL-8 production in HGEC stimulated with these bacterial components was clearly inhibited by mouse monoclonal antibody to human TLR2. These findings suggest that P. gingivalis fimbrial protein and its active peptide are capable of activating HGEC through TLR2.
Figures
References
-
- Akashi S, Ogata H, Kirikae F, Kirikae T, Kawasaki K, Nishijima M, Shimazu R, Nagai Y, Fukudome K, Kimoto M, Miyake K. Regulatory roles for CD14 and phosphatidylinositol in the signaling via Toll-like receptor 4-MD-2. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2000;168:172–177. - PubMed
-
- Aliprantis A O, Yang R B, Mark M R, Suggett S, Devaux B, Radolf J D, Klimpel G R, Godowski P, Zychlinsky A. Cell activation and apoptosis by bacterial lipoproteins through toll-like receptor-2. Science. 1999;285:736–739. - PubMed
-
- Böyum A. Isolation of mononuclear cells and granulocytes from human blood. Scand J Clin Lab Investig. 1968;97:77–89. - PubMed
-
- Brightbill H D, Libraty D H, Krutzik S R, Yang R B, Belisle J T, Bleharski J R, Maitland M, Norgard M V, Plevy S E, Smale S T, Brennan P J, Bloom B R, Godowski P J, Modlin R L. Host defense mechanisms triggered by microbial lipoproteins through toll-like receptors. Science. 1999;285:732–736. - PubMed
-
- Cario E, Rosenberg I M, Brandwein S L, Beck P L, Reinecker H-C, Podolsky D K. Lipopolysaccharide activates distinct signaling pathways in intestinal epithelial cell lines expressing Toll-like receptors. J Immunol. 2000;164:966–972. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

