Dynamic changes in neutrophil defensins during endotoxemia
- PMID: 11705961
- PMCID: PMC98875
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.69.12.7793-7799.2001
Dynamic changes in neutrophil defensins during endotoxemia
Abstract
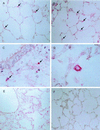
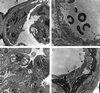
Bacterial endotoxin or lipopolysaccharide (LPS) is an important causative agent of sepsis. This study determines the expression of defensins NP-2 and NP-5 and the function of polymorphonuclear leukocytes (PMN) in rabbits treated with LPS. PMN functional activity was assessed by measuring CD18 expression and H(2)O(2) production and by examining the lungs. NP-2 and, to a minor extent, NP-5 of circulating PMN increase during endotoxemia. This early increase is concomitant with neutrophilia and elevated CD18 expression and H(2)O(2) production, as well as with enhanced NP-2 immunoreactivity in pulmonary microvessels. A decline in defensins, shortly after the last LPS treatment, is associated with a decrease in the circulating activated PMN and enhanced immunoreactivity in the inflammatory cells, as well as with lung tissue damage. This study shows that LPS-induced changes in the defensins of circulating PMN correlate with the number and activated condition of these cells and suggests that PMN-derived products implement the inflammatory reaction that leads to lung injury and sepsis.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Neutrophil structural changes associated with chronic endotoxemia and lung injury.J Inflamm. 1998;48(1):1-12. J Inflamm. 1998. PMID: 9368188
-
Inhibition of pulmonary neutrophil trafficking during endotoxemia is dependent on the stimulus for migration.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1999 Apr;20(4):769-76. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb.20.4.3481. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1999. PMID: 10101010
-
Antibacterial proteins of granulocytes differ in interaction with endotoxin. Comparison of bactericidal/permeability-increasing protein, p15s, and defensins.J Immunol. 1995 May 15;154(10):5403-10. J Immunol. 1995. PMID: 7730641
-
[Effects of human i.v. immunoglobulin on bacterial clearance and granulocyte function in endotoxinemia].Anasthesiol Intensivmed Notfallmed Schmerzther. 1997 Jul;32(7):420-5. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-995083. Anasthesiol Intensivmed Notfallmed Schmerzther. 1997. PMID: 9340030 German.
-
Neutrophil migration during endotoxemia.J Leukoc Biol. 1999 Jul;66(1):10-24. doi: 10.1002/jlb.66.1.10. J Leukoc Biol. 1999. PMID: 10410985 Review.
Cited by
-
Neutrophil alpha-defensins cause lung injury by disrupting the capillary-epithelial barrier.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2010 May 1;181(9):935-46. doi: 10.1164/rccm.200907-1128OC. Epub 2010 Jan 21. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2010. PMID: 20093642 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ashitani J, Mukae H, Ihiboshi H, Taniguchi H, Mashimoto H, Nakazato M, Matsukura S. Defensin in plasma and in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid from patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome. Nihon Kyobu Shikkan Gakkai Zasshi. 1996;34:1349–1353. - PubMed
-
- Ashitani J, Mukae H, Nakazato M, Ihi T, Mashimoto H, Kadota J, Kohno S, Matsukura S. Elevated concentrations of defensins in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid in diffuse panbronchiolitis. Eur Respir J. 1998;11:104–111. - PubMed
-
- Bradley S G. Cellular and molecular mechanisms of action of bacterial endotoxins. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1979;33:67–94. - PubMed
-
- Chasovnikova L V, Formaziuk V E, Sergienko V I, Kokriakov V N. Interaction of myeloperoxidase and defensins with lipid monolayers. Biokhimiia. 1992;57:97–102. - PubMed
-
- Diamond G, Bevins C L. Beta-defensins: endogenous antibiotics of the innate host defense response. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1998;88:221–225. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

