Evaluation of a tetracycline-inducible promoter in Staphylococcus aureus in vitro and in vivo and its application in demonstrating the role of sigB in microcolony formation
- PMID: 11705967
- PMCID: PMC98881
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.69.12.7851-7857.2001
Evaluation of a tetracycline-inducible promoter in Staphylococcus aureus in vitro and in vivo and its application in demonstrating the role of sigB in microcolony formation
Abstract
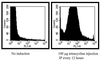
An inducible promoter system provides a powerful tool for studying the genetic basis for virulence. A variety of inducible systems have been used in other organisms, including pXyl-xylR-inducible promoter, the pSpac-lacI system, and the arabinose-inducible P(BAD) promoter, but each of these systems has limitations in its application to Staphylococcus aureus. In this study, we demonstrated the efficacy of a tetracycline-inducible promoter system in inducing gene expression in S. aureus in vitro and inside epithelial cells as well as in an animal model of infection. Using the xyl/tetO promoter::gfp(uvr) fusion carried on a shuttle plasmid, we demonstrated that dose-dependent tetracycline induction, as measured by bacterial fluorescence, occurred in each of the above environments while basal activation under noninduced conditions remained low. To ascertain how the system can be used to elucidate the genetic basis of a pathogenic phenotype, we cloned the sigB gene downstream of the inducible promoter. Induction of SigB expression led to dose-dependent attachment of the tested strain to polystyrene microtiter wells. Additionally, bacterial microcolony formation, an event preceding mature biofilm formation, also increased with tetracycline induction of SigB.
Figures


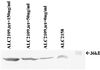
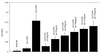

References
-
- Blake M S, Johnston K H, Russell-Jones G J, Gotschlich E C. A rapid sensitive method for detection of alkaline phosphatase-conjugated anti-antibody on Western blots. Anal Biochem. 1984;136:175–179. - PubMed
-
- Boyce J M. Epidemiology and prevention of nosocomial infections. In: Crossley K B, Archer G L, editors. The staphylococci in human disease. New York, N.Y: Churchill Livingstone; 1997. pp. 309–329.
-
- Chien Y, Cheung A L. Molecular interactions between two global regulators. sar and agr, in Staphylococcus aureus. J Biol Chem. 1998;274:2645–2652. - PubMed
-
- Costerton J W, Stewart P S, Greenberg E P. Bacterial biofilms: a common cause of persistent infections. Science. 1999;284:1318–1322. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

