Toxoplasma gondii myosins B/C: one gene, two tails, two localizations, and a role in parasite division
- PMID: 11706051
- PMCID: PMC2198869
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200012116
Toxoplasma gondii myosins B/C: one gene, two tails, two localizations, and a role in parasite division
Abstract
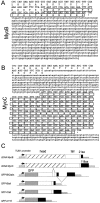
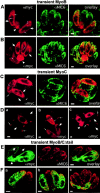
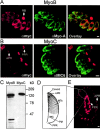
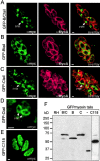
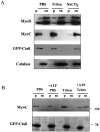
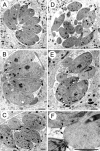
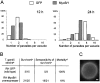
In apicomplexan parasites, actin-disrupting drugs and the inhibitor of myosin heavy chain ATPase, 2,3-butanedione monoxime, have been shown to interfere with host cell invasion by inhibiting parasite gliding motility. We report here that the actomyosin system of Toxoplasma gondii also contributes to the process of cell division by ensuring accurate budding of daughter cells. T. gondii myosins B and C are encoded by alternatively spliced mRNAs and differ only in their COOH-terminal tails. MyoB and MyoC showed distinct subcellular localizations and dissimilar solubilities, which were conferred by their tails. MyoC is the first marker selectively concentrated at the anterior and posterior polar rings of the inner membrane complex, structures that play a key role in cell shape integrity during daughter cell biogenesis. When transiently expressed, MyoB, MyoC, as well as the common motor domain lacking the tail did not distribute evenly between daughter cells, suggesting some impairment in proper segregation. Stable overexpression of MyoB caused a significant defect in parasite cell division, leading to the formation of extensive residual bodies, a substantial delay in replication, and loss of acute virulence in mice. Altogether, these observations suggest that MyoB/C products play a role in proper daughter cell budding and separation.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Plasticity between MyoC- and MyoA-glideosomes: an example of functional compensation in Toxoplasma gondii invasion.PLoS Pathog. 2014 Nov 13;10(10):e1004504. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1004504. eCollection 2014 Oct. PLoS Pathog. 2014. PMID: 25393004 Free PMC article.
-
A novel class of unconventional myosins from Toxoplasma gondii.J Mol Biol. 1997 Aug 8;271(1):139-46. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1997.1167. J Mol Biol. 1997. PMID: 9300060
-
TgTKL1 Is a Unique Plant-Like Nuclear Kinase That Plays an Essential Role in Acute Toxoplasmosis.mBio. 2018 Mar 20;9(2):e00301-18. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00301-18. mBio. 2018. PMID: 29559568 Free PMC article.
-
Microneme proteins: structural and functional requirements to promote adhesion and invasion by the apicomplexan parasite Toxoplasma gondii.Int J Parasitol. 2001 Oct;31(12):1293-302. doi: 10.1016/s0020-7519(01)00257-0. Int J Parasitol. 2001. PMID: 11566297 Review.
-
Migration of Toxoplasma gondii across biological barriers.Trends Microbiol. 2003 Sep;11(9):426-30. doi: 10.1016/s0966-842x(03)00205-1. Trends Microbiol. 2003. PMID: 13678858 Review.
Cited by
-
A novel multifunctional oligonucleotide microarray for Toxoplasma gondii.BMC Genomics. 2010 Oct 25;11:603. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-11-603. BMC Genomics. 2010. PMID: 20974003 Free PMC article.
-
Viability and infectivity of Toxoplasma gondii tachyzoites exposed to Butanedione monoxime.J Parasit Dis. 2020 Dec;44(4):822-828. doi: 10.1007/s12639-020-01259-9. Epub 2020 Aug 17. J Parasit Dis. 2020. PMID: 32837055 Free PMC article.
-
Myosin A and F-Actin play a critical role in mitochondrial dynamics and inheritance in Toxoplasma gondii.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Mar 18:2024.03.18.585462. doi: 10.1101/2024.03.18.585462. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: PLoS Pathog. 2024 Oct 7;20(10):e1012127. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1012127. PMID: 38562694 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Calmodulin-like proteins localized to the conoid regulate motility and cell invasion by Toxoplasma gondii.PLoS Pathog. 2017 May 5;13(5):e1006379. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1006379. eCollection 2017 May. PLoS Pathog. 2017. PMID: 28475612 Free PMC article.
-
Contribution of the residual body in the spatial organization of Toxoplasma gondii tachyzoites within the parasitophorous vacuole.J Biomed Biotechnol. 2011;2011:473983. doi: 10.1155/2011/473983. Epub 2011 Nov 28. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2011. PMID: 22190852 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ajioka, J.W., J.C. Boothroyd, B.P. Brunk, A. Hehl, L. Hiller, I.D. Manger, G.C. Overton, M. Marrra, D. Roos, K.-L. Wan, et al. 1998. Gene discovery by EST sequencing in Toxoplasma gondii reveals sequences restricted to the Apicomplexa. Genome Res. 8:18–28. - PubMed
-
- Bezanilla, M., J.M. Wilson, and T.D. Pollard. 2000. Fission yeast myosin-II isoforms assemble into contractile rings at distinct times during mitosis. Curr. Biol. 10:397–400. - PubMed
-
- Ding, M., C. Clayton, and D. Soldati. 2000. Toxoplasma gondii catalase: are there peroxisomes in Toxoplasma? J. Cell Sci. 113:2409–2419. - PubMed
-
- Dobrowolski, J., and L.D. Sibley. 1997. The role of the cytoskeleton in host cell invasion by Toxoplasma gondii. Behring Inst. Mitt. 99:90–96. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions

