Myosin V exhibits a high duty cycle and large unitary displacement
- PMID: 11706052
- PMCID: PMC2198872
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200103128
Myosin V exhibits a high duty cycle and large unitary displacement
Abstract
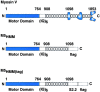
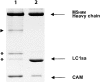
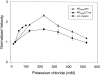
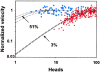
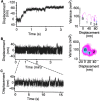
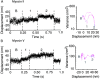
Myosin V is a double-headed unconventional myosin that has been implicated in organelle transport. To perform this role, myosin V may have a high duty cycle. To test this hypothesis and understand the properties of this molecule at the molecular level, we used the laser trap and in vitro motility assay to characterize the mechanics of heavy meromyosin-like fragments of myosin V (M5(HMM)) expressed in the Baculovirus system. The relationship between actin filament velocity and the number of interacting M5(HMM) molecules indicates a duty cycle of > or =50%. This high duty cycle would allow actin filament translocation and thus organelle transport by a few M5(HMM) molecules. Single molecule displacement data showed predominantly single step events of 20 nm and an occasional second step to 37 nm. The 20-nm unitary step represents the myosin V working stroke and is independent of the mode of M5(HMM) attachment to the motility surface or light chain content. The large M5(HMM) working stroke is consistent with the myosin V neck acting as a mechanical lever. The second step is characterized by an increased displacement variance, suggesting a model for how the two heads of myosin V function in processive motion.
Figures




References
-
- Baker, J.P., and M.A. Titus. 1998. Myosins: matching functions with motors. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 10:80–86. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

