Diversity of Arabidopsis genes encoding precursors for phytosulfokine, a peptide growth factor
- PMID: 11706167
- PMCID: PMC129256
Diversity of Arabidopsis genes encoding precursors for phytosulfokine, a peptide growth factor
Abstract
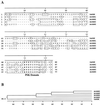
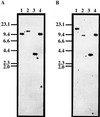
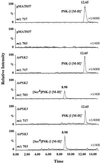
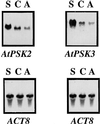
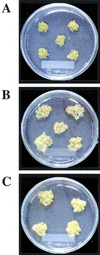
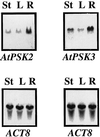
Phytosulfokine-alpha (PSK-alpha), a unique plant peptide growth factor, was originally isolated from conditioned medium of asparagus (Asparagus officinalis) mesophyll cell cultures. PSK-alpha has several biological activities including promoting plant cell proliferation. Four genes that encode precursors of PSK-alpha have been identified from Arabidopsis. Analysis of cDNAs for two of these, AtPSK2 and AtPSK3, shows that both of these genes consist of two exons and one intron. The predicted precursors have N-terminal signal peptides and only a single PSK-alpha sequence located close to their carboxyl termini. Both precursors contain dibasic processing sites flanking PSK, analogous to animal and yeast prohormones. Although the PSK domain including the sequence of PSK-alpha and three amino acids preceding it are perfectly conserved, the precursors bear very limited similarity among Arabidopsis and rice (Oryza sativa), suggesting a new level of diversity among polypeptides that are processed into the same signaling molecule in plants, a scenario not found in animals and yeast. Unnatural [serine-4]PSK-beta was found to be secreted by transgenic Arabidopsis cells expressing a mutant of either AtPSK2 or AtPSK3 cDNAs, suggesting that both AtPSK2 and AtPSK3 encode PSK-alpha precursors. AtPSK2 and AtPSK3 were expressed demonstrably not only in cultured cells but also in intact plants, suggesting that PSK-alpha may be essential for plant cell proliferation in vivo as well as in vitro. Overexpression of either precursor gene allowed the transgenic calli to grow twice as large as the controls. However, the transgenic cells expressing either antisense cDNA did not dramatically decrease mitogenic activity, suggesting that these two genes may act redundantly.
Figures


References
-
- Brand U, Fletcher JC, Hobe M, Meyerowitz EM, Simon R. Dependence of stem cell fate in Arabidopsis on a feedback loop regulated by CLV3 activity. Science. 2000;289:617–619. - PubMed
-
- Chomczynski P. A reagent for the single-step simultaneous isolation of RNA, DNA and proteins from cell and tissue samples. BioTechniques. 1993;15:532–536. - PubMed
-
- Clark SE, Williams RW, Meyerowitz EM. The CLAVATA1 gene encodes a putative receptor kinase that controls shoot and floral meristem size in Arabidopsis. Cell. 1997;89:575–585. - PubMed
-
- Dorner AJ, Kaufman RJ. Analysis of synthesis, processing, and secretion of proteins expressed in mammalian cells. Methods Enzymol. 1990;185:577–598. - PubMed
-
- Fletcher JC, Brand U, Running MP, Simon R, Meyerowitz EM. Signaling of cell fate decisions by CLAVATA3 in Arabidopsis shoot meristems. Science. 1999;283:1911–1914. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
