Pause and rotation of F(1)-ATPase during catalysis
- PMID: 11707579
- PMCID: PMC61095
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.241365698
Pause and rotation of F(1)-ATPase during catalysis
Abstract
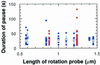
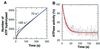
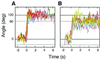
F(1)-ATPase is a rotary motor enzyme in which a single ATP molecule drives a 120 degrees rotation of the central gamma subunit relative to the surrounding alpha(3)beta(3) ring. Here, we show that the rotation of F(1)-ATPase spontaneously lapses into long (approximately 30 s) pauses during steady-state catalysis. The effects of ADP-Mg and mutation on the pauses, as well as kinetic comparison with bulk-phase catalysis, strongly indicate that the paused enzyme corresponds to the inactive state of F(1)-ATPase previously known as the ADP-Mg inhibited form in which F(1)-ATPase fails to release ADP-Mg from catalytic sites. The pausing position of the gamma subunit deviates from the ATP-waiting position and is most likely the recently found intermediate 90 degrees position.
Figures


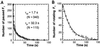

References
-
- Deckers-Hebestreit G, Altendlf K. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1996;50:791–824. - PubMed
-
- Boyer P D. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2000;1458:252–262. - PubMed
-
- Weber J, Senior A E. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2000;1458:300–309. - PubMed
-
- Cross R L. Biochem Biophys Acta. 2000;1458:270–275. - PubMed
-
- Abrahams J P, Leslie A G, Lutter R, Walker J E. Nature (London) 1994;370:621–628. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

