SNAP-29: a general SNARE protein that inhibits SNARE disassembly and is implicated in synaptic transmission
- PMID: 11707603
- PMCID: PMC61163
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.251532398
SNAP-29: a general SNARE protein that inhibits SNARE disassembly and is implicated in synaptic transmission
Abstract
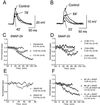
Using the yeast two-hybrid system with syntaxin-1A as bait, we isolated soluble NSF attachment protein (SNAP)-29 from a human brain cDNA library. Synaptosomal fractionation and immunocytochemical staining of hippocampal neurons in culture showed that SNAP-29 is present at synapses and is predominantly associated with synaptic vesicles. The interaction of SNAP-29 with syntaxin-1 was further confirmed with immunoprecipitation analysis. Binding competition studies with SNAP-29 demonstrated that it could compete with alpha-SNAP for binding to synaptic SNAP receptors (SNAREs) and consequently inhibit disassembly of the SNARE complex. Introduction of SNAP-29 into presynaptic superior cervical ganglion neurons in culture significantly inhibited synaptic transmission in an activity-dependent manner. Although SNAP-29 has been suggested to be a general SNARE component in membrane trafficking, our findings suggest that it may function as a regulator of SNARE complex disassembly and modulate the process of postfusion recycling of the SNARE components.
Figures





References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

