Synergy, pharmacodynamics, and time-sequenced ultrastructural changes of the interaction between nikkomycin Z and the echinocandin FK463 against Aspergillus fumigatus
- PMID: 11709302
- PMCID: PMC90831
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.45.12.3310-3321.2001
Synergy, pharmacodynamics, and time-sequenced ultrastructural changes of the interaction between nikkomycin Z and the echinocandin FK463 against Aspergillus fumigatus
Abstract
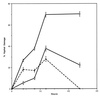
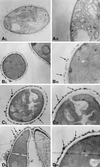
We investigated the potential synergy between two cell wall-active agents, the echinocandin FK463 (FK) and the chitin synthase inhibitor nikkomycin Z (NZ), against 16 isolates of filamentous fungi. Susceptibility testing was performed with a broth macrodilution procedure by NCCLS methods. The median minimal effective concentration (MEC) of FK against all Aspergillus species was 0.25 microg/ml (range, 0.05 to 0.5 microg/ml). For Fusarium solani and Rhizopus oryzae, MECs of FK were >512 microg/ml. The median MEC of NZ against Aspergillus fumigatus was 32 microg/ml (range, 8 to 64 microg/ml), and that against R. oryzae was 0.5 microg/ml (range, 0.06 to 2 microg/ml); however, for the other Aspergillus species, as well as F. solani, MECs were >512 microg/ml. A checkerboard inhibitory assay demonstrated synergy against A. fumigatus (median fractional inhibitory concentration index = 0.312 [range, 0.15 to 0.475]). The effect was additive to indifferent against R. oryzae and indifferent against other Aspergillus spp. and F. solani. We further investigated the pharmacodynamics of hyphal damage by MTT [3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide] assay and examined the time-sequenced changes in hyphal ultrastructure. Significant synergistic hyphal damage was demonstrated with the combination of NZ (2 to 32 microg/ml) and FK (0.03 to 0.5 microg/ml) over a wide range of concentrations (P < 0.001). The synergistic effect was most pronounced after 12 h of incubation and was sustained through 24 h. Time-sequenced light and electron microscopic studies demonstrated that structural alterations of hyphae were profound, with marked transformation of hyphae to blastospore-like structures, in the presence of FK plus NZ, while fungi treated with a single drug showed partial recovery at 24 h. The methods used in this study may be applicable to elucidating the activity and interaction of other cell wall-active agents. In summary, these two cell wall-targeted antifungal agents, FK and NZ, showed marked time-dependent in vitro synergistic activity against A. fumigatus.
Figures






References
-
- Chiou C C, Groll A H, Walsh T J. New drugs and novel targets for treatment of invasive fungal infections in patients with cancer. Oncologist. 2000;5:120–135. - PubMed
-
- Denning D W. Therapeutic outcome in invasive aspergillosis. Clin Infect Dis. 1996;23:608–615. - PubMed
-
- Elorza M V, Murgui A, Rico H, Miragall F, Sentandreu R. Formation of a new cell wall by protoplasts of Candida albicans: effect of papulacandin B, tunicamycin and Nikkomycin. J Gen Microbiol. 1987;133:2315–2325. - PubMed
-
- Garcia-Rodriguez L J, Trilla J A, Castro C, Valdivieso M H, Duran A, Roncero C. Characterization of the chitin biosynthesis process as a compensatory mechanism in the fks1 mutant of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. FEBS Lett. 2000;28:84–88. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

