Resistance-nodulation-cell division-type efflux pump involved in aminoglycoside resistance in Acinetobacter baumannii strain BM4454
- PMID: 11709311
- PMCID: PMC90840
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.45.12.3375-3380.2001
Resistance-nodulation-cell division-type efflux pump involved in aminoglycoside resistance in Acinetobacter baumannii strain BM4454
Abstract
Multidrug-resistant strain Acinetobacter baumannii BM4454 was isolated from a patient with a urinary tract infection. The adeB gene, which encodes a resistance-nodulation-cell division (RND) protein, was detected in this strain by PCR with two degenerate oligodeoxynucleotides. Insertional inactivation of adeB in BM4454, which generated BM4454-1, showed that the corresponding protein was responsible for aminoglycoside resistance and was involved in the level of susceptibility to other drugs including fluoroquinolones, tetracyclines, chloramphenicol, erythromycin, trimethoprim, and ethidium bromide. Study of ethidium bromide accumulation in BM4454 and BM4454-1, in the presence or in the absence of carbonyl cyanide m-chlorophenylhydrazone, demonstrated that AdeB was responsible for the decrease in intracellular ethidium bromide levels in a proton motive force-dependent manner. The adeB gene was part of a cluster that included adeA and adeC which encodes proteins homologous to membrane fusion and outer membrane proteins of RND-type three-component efflux systems, respectively. The products of two upstream open reading frames encoding a putative two-component regulatory system might be involved in the regulation of expression of the adeABC gene cluster.
Figures
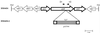

References
-
- Ahmed M, Borsch C M, Taylor S S, Vazquez-Laslop N, Neyfakh A A. A protein that activates expression of a multidrug efflux transporter upon binding the transporter substrates. J Biol Chem. 1994;269:28506–28513. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

