Low dose balsalazide (1.5 g twice daily) and mesalazine (0.5 g three times daily) maintained remission of ulcerative colitis but high dose balsalazide (3.0 g twice daily) was superior in preventing relapses
- PMID: 11709512
- PMCID: PMC1728533
- DOI: 10.1136/gut.49.6.783
Low dose balsalazide (1.5 g twice daily) and mesalazine (0.5 g three times daily) maintained remission of ulcerative colitis but high dose balsalazide (3.0 g twice daily) was superior in preventing relapses
Abstract
Background: Balsalazide is a new 5-aminosalicylic acid (5-ASA) containing prodrug. Its efficacy in comparison with standard mesalazine therapy and the optimum dose for maintaining remission of ulcerative colitis are still unclear.
Aims: To compare the relapse preventing effect and safety profile of two doses of balsalazide and a standard dose of Eudragit coated mesalazine.
Methods: A total of 133 patients with ulcerative colitis in remission were recruited to participate in a double blind, multicentre, randomised trial: 49 patients received balsalazide 1.5 g twice daily, 40 received balsalazide 3.0 g twice daily, and 44 received mesalazine 0.5 g three times daily. Efficacy assessments were clinical activity index (CAI) and endoscopic score according to Rachmilewitz, and a histological score. In addition, laboratory tests were performed and urinary excretion of 5-ASA and its metabolite N-Ac-5-ASA was analysed. The study lasted for 26 weeks.
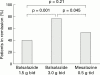
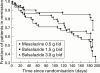
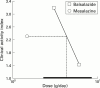
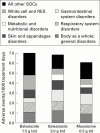
Results: Balsalazide 3.0 g twice daily resulted in a significantly higher clinical remission rate (77.5%) than balsalazide 1.5 g twice daily (43.8%) and mesalazine 0.5 g three times daily (56.8%) (p=0.006). The respective times to relapse were 161 days, 131 days (p=0.003), and 144 days (NS). Accordingly, pairwise contrasts of the final endoscopic score demonstrated a significant difference (p=0.005) between the two balsalazide treatment groups while differences between either of these two groups and mesalazine were not statistically significant. Patients treated with balsalazide excreted less 5-ASA and N-Ac-5-ASA than patients receiving mesalazine but these differences were not statistically significant. Discontinuation of the trial because of adverse effects occurred in nine patients: three in the balsalazide 1.5 g twice daily group, two in the balsalazide 3.0 g twice daily group, and four in the mesalazine 0.5 g three times daily group. No clinically important new drug safety related findings were identified in this study.
Conclusions: High dose balsalazide (3.0 g twice daily) was superior in maintaining remission in patients with ulcerative colitis compared with a low dose (1.5 g twice daily) or a standard dose of mesalazine (0.5 g three times daily). All three treatments were safe and well tolerated.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
