Carbamazepine reduces memory induced activation of mesial temporal lobe structures: a pharmacological fMRI-study
- PMID: 11710962
- PMCID: PMC59836
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2377-1-6
Carbamazepine reduces memory induced activation of mesial temporal lobe structures: a pharmacological fMRI-study
Abstract
Background and purpose: It is not known whether carbamazepine (CBZ; a drug widely used in neurology and psychiatry) influences the blood oxygenation level dependent (BOLD) contrast changes induced by neuronal activation and measured by functional MRI (fMRI). We aimed to investigate the influence of CBZ on memory induced activation of the mesial temporal lobes in patients with symptomatic temporal lobe epilepsy (TLE).
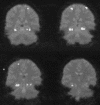
Material and methods: Twenty-one individual patients with refractory symptomatic TLE with different CBZ serum levels and 20 healthy controls were studied using BOLD fMRI. Mesial temporal lobe (MTL) activation was induced by a task that is based on the retrieval of individually familiar visuo-spatial knowledge. The extent of significant MTL fMRI activation was measured and correlated with the CBZ serum level.
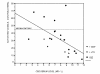
Results: In TLE patients, the extent of significant fMRI activation over both MTL was negatively correlated to the CBZ serum level (Spearman r = -0.654, P < 0.001). Activation over the supposedly normal MTL, i.e. contralateral to the seizure onset of TLE patients, was smaller than the averaged MTL activation in healthy controls (P < 0.005). Age, duration of epilepsy, side of seizure onset, and intelligence were not correlated to the extent of the significant BOLD-response over both MTL in patients with TLE.
Conclusions: In TLE patients, carbamazepine reduces the fMRI-detectable changes within the mesial temporal lobes as induced by effortful memory retrieval. FMRI appears to be suitable to study the effects of chronic drug treatment in patients with epilepsy.
Figures
References
-
- Detre JA, Maccotta L, King D, et al. Functional MRI lateralization of memory in temporal lobe epilepsy. Neurology. 1998;50:926–32. - PubMed
-
- May A, Bahra A, Büchel C, Turner R, Goadsby PJ. Functional magnetic resonance imaging in spontaneous attacks of SUNCT: short-lasting neuralgiform headache with conjunctival injection and tearing. Ann Neurol. 1999;46:791–794. doi: 10.1002/1531-8249(199911)46:5<791::AID-ANA18>3.0.CO;2-8. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Mattson RH, Cramer JA, Collins JF, et al. A comparison of valproate and carbamazepine for the treatment of complex partial seizures and secondarily generalized tonic-clonic seizures in adults. N Engl J Med. 1992;327:765–771. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

