TIF1beta functions as a coactivator for C/EBPbeta and is required for induced differentiation in the myelomonocytic cell line U937
- PMID: 11711437
- PMCID: PMC312827
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.937201
TIF1beta functions as a coactivator for C/EBPbeta and is required for induced differentiation in the myelomonocytic cell line U937
Retraction in
-
Retraction.Genes Dev. 2002 Aug 15;16(16):2170. Genes Dev. 2002. PMID: 12269264 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
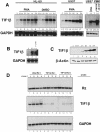
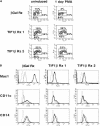
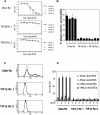
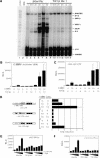
Representational difference analysis (RDA) cloning has identified transcriptional intermediary factor 1 beta (TIF1beta) as a gene inducibly expressed early during myeloid differentiation of the promyelocytic cell lines HL-60 and U937. To assess the role of TIF1beta, U937 cell lines were made that expressed antisense-hammerhead ribozymes targeted specifically against TIF1beta mRNA. These cells failed to differentiate into macrophages, as determined by several criteria: a nonadherent morphology, a failure to arrest cell cycle, lowered levels of macrophage-specific cell surface markers, resistance to Legionella pneumophila infection, a loss of the ability to phagocytose and chemotax, and decreased expression of chemokine mRNAs. One way TIF1beta acts in macrophage differentiation is to augment C/EBPbeta transcriptional activity. Furthermore, we show by EMSA supershifts and coimmunoprecipitation that C/EBPbeta and TIF1beta physically interact. Although TIF1beta is necessary for macrophage differentiation of U937 cells, it is not sufficient, based on the inability of ectopically expressed TIF1beta to induce or augment phorbol ester-induced macrophage differentiation. We conclude that TIF1beta plays an important role in the terminal differentiation program of macrophages, which involves the coactivation of C/EBPbeta and induction of C/EBPbeta-responsive myeloid genes.
Figures


Comment in
-
Findings of scientific misconduct.NIH Guide Grants Contracts (Bethesda). 2003 Jun 30:NOT-OD-03-050. NIH Guide Grants Contracts (Bethesda). 2003. PMID: 12841202 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Monocyte differentiation to macrophage requires interferon regulatory factor 7.J Biol Chem. 2001 Nov 30;276(48):45491-6. doi: 10.1074/jbc.C100421200. Epub 2001 Oct 3. J Biol Chem. 2001. PMID: 11585813
-
Coactivator TIF1beta interacts with transcription factor C/EBPbeta and glucocorticoid receptor to induce alpha1-acid glycoprotein gene expression.Mol Cell Biol. 1998 Oct;18(10):5880-7. doi: 10.1128/MCB.18.10.5880. Mol Cell Biol. 1998. PMID: 9742105 Free PMC article.
-
PE-1/METS, an antiproliferative Ets repressor factor, is induced by CREB-1/CREM-1 during macrophage differentiation.J Biol Chem. 2004 Apr 23;279(17):17772-84. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M311991200. Epub 2004 Jan 30. J Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 14754893
-
IRF-2 is involved in up-regulation of nonmuscle myosin heavy chain II-A gene expression during phorbol ester-induced promyelocytic HL-60 differentiation.J Biol Chem. 2004 Dec 31;279(53):56042-52. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M404791200. Epub 2004 Oct 20. J Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 15496418
-
[KAP-1, a scaffold protein in transcription regulation].Yi Chuan. 2007 Feb;29(2):131-6. doi: 10.1360/yc-007-0131. Yi Chuan. 2007. PMID: 17369165 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
The transcription intermediary factor 1β coactivates the androgen receptor.J Endocrinol Invest. 2013 Oct;36(9):699-706. doi: 10.3275/8927. Epub 2013 Apr 8. J Endocrinol Invest. 2013. PMID: 23563173
-
Dynamic changes in ribosome-associated proteome and phosphoproteome during deoxynivalenol-induced translation inhibition and ribotoxic stress.Toxicol Sci. 2014 Mar;138(1):217-33. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kft270. Epub 2013 Nov 27. Toxicol Sci. 2014. PMID: 24284785 Free PMC article.
-
Proteomic analysis of embryonic kidney development: Heterochromatin proteins as epigenetic regulators of nephrogenesis.Sci Rep. 2015 Sep 11;5:13951. doi: 10.1038/srep13951. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 26359909 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting Nrf2 in healthy and malignant ovarian epithelial cells: Protection versus promotion.Mol Oncol. 2015 Aug;9(7):1259-73. doi: 10.1016/j.molonc.2015.03.003. Epub 2015 Mar 19. Mol Oncol. 2015. PMID: 25841766 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of an artificial zinc finger epigenetic modulator: widespread binding but limited regulation.Nucleic Acids Res. 2014;42(16):10856-68. doi: 10.1093/nar/gku708. Epub 2014 Aug 13. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014. PMID: 25122745 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aasland R, Gibson TJ, Stewart AF. The PHD finger: Implication for chromatin-mediated transcriptional regulation. Trends Biochem Sci. 1995;20:56–59. - PubMed
-
- Aderem A, Underhill DM. Mechanisms of phagocytosis in macrophages. Annu Rev Immunol. 1999;17:593–623. - PubMed
-
- Agata Y, Matsuda E, Shimizu A. Two novel Kruppel-associated box-containing zinc-finger proteins, KRAZ1 and KRAZ2, repress transcription through functional interaction with the corepressor KAP-1 (TIF1β/KRIP-1) J Biol Chem. 1999;274:16412–16422. - PubMed
-
- Akira S. IL-6-regulated transcription factors. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 1997;29:1401–1418. - PubMed
-
- Akira S, Kishimoto T. IL-6 and NF-IL6 in acute-phase response and viral infection. Immunol Rev. 1992;127:25–50. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
