Rapid and non-genomic reduction of intracellular [Ca(2+)] induced by aldosterone in human bronchial epithelium
- PMID: 11711579
- PMCID: PMC2278946
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.2001.0267k.x
Rapid and non-genomic reduction of intracellular [Ca(2+)] induced by aldosterone in human bronchial epithelium
Abstract
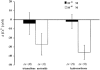
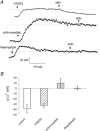
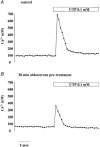
1. Using a Ca(2+) imaging system and fura-2 AM (5 microM) we showed that exposure of polarised monolayers of human bronchial epithelial cells (16HBE14o- cell line) to aldosterone produced a fast intracellular [Ca(2+)] ([Ca(2+)](i)) decrease, in 70 % of cells. Exposure to aldosterone (1 nM) reduced the [Ca(2+)](i) by 39 +/- 9 nM (n = 282, P < 0.0001) within 10 min, from a basal [Ca(2+)](i) of 131 +/- 19 nM (n = 282). 2. The effect of aldosterone on [Ca(2+)](i) was not affected by inhibitors of the classical genomic pathway, cycloheximide (1 microM) or spironolactone (10 microM). The aldosterone-induced [Ca(2+)](i) decrease was inhibited by thapsigargin (1 microM), pertussis toxin (24 h at 200 ng ml(-1)), the adenylate cyclase inhibitors 2',3'-dideoxyadenosine (200 microM) and MDL-12,330A hydrochloride (500 microM), and the protein kinase A inhibitor R(P)-adenosine 3',5'-cyclic monophosphorothioate (200 microM). In addition, treatment of 16HBE14o- monolayers with aldosterone (1 nM) inhibited by approximately 30 % the large and transient [Ca(2+)](i) increase induced by apical exposure to uridine triphosphate (UTP, 0.1 mM), a known secretagogue in airway epithelia. 3. Our results demonstrate for the first time that in human bronchial epithelial cells, aldosterone decreases [Ca(2+)](i) levels via a non-genomic mechanism. The hormone-induced changes to [Ca(2+)](i) involve stimulation of thapsigargin-sensitive Ca(2+)-ATPase, via G-protein-, adenylate cyclase- and protein kinase A-coupled signalling pathways.
Figures

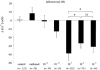


References
-
- Al-Dujaili EA, Edwards CR. The development and application of a direct radioimmunoassay for plasma aldosterone using 125I-labeled ligand-comparison of three methods. Journal of Clinical Endocrinology Metabolism. 1978;46:105–113. - PubMed
-
- Ballard PL, Baxter JD, Higgins SJ, Rousseau GG, Tomkins GM. General presence of glucocorticoid receptors in mammalian tissues. Endocrinology. 1974;94:998–1002. - PubMed
-
- Chabra SK, Khanduja A, Jain D. Decreasing sodium-potassium and calcium adenosine triphosphatase activity in asthma: modulation by inhaled and oral corticosteroids. Indian Journal of Chest Disease and Allied Sciences. 1999;41:15–26. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

