Double-stranded RNA-mediated interference with plant virus infection
- PMID: 11711619
- PMCID: PMC116125
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.75.24.12288-12297.2001
Double-stranded RNA-mediated interference with plant virus infection
Abstract
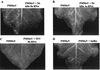
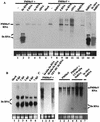
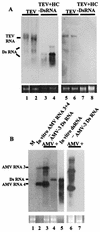
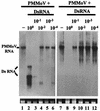
Double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) has been shown to play a key role as an inducer of different interference phenomena occurring in both the plant and animal kingdoms. Here, we show that dsRNA derived from viral sequences can interfere with virus infection in a sequence-specific manner by directly delivering dsRNA to leaf cells either by mechanical inoculation or via an Agrobacterium-mediated transient-expression assay. We have successfully interfered with the infection of plants by three viruses belonging to the tobamovirus, potyvirus, and alfamovirus groups, demonstrating the reliability of the approach. We suggest that the effect mediated by dsRNA in plant virus infection resembles the analogous phenomenon of RNA interference observed in animals. The interference observed is sequence specific, is dose dependent, and is triggered by dsRNA but not single-stranded RNA. Our results support the view that a dsRNA intermediate in virus replication acts as efficient initiator of posttranscriptional gene silencing (PTGS) in natural virus infections, triggering the initiation step of PTGS that targets viral RNA for degradation.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Transient expression of homologous hairpin RNA causes interference with plant virus infection and is overcome by a virus encoded suppressor of gene silencing.Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2003 Feb;16(2):149-58. doi: 10.1094/MPMI.2003.16.2.149. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2003. PMID: 12575749
-
Crude extracts of bacterially expressed dsRNA can be used to protect plants against virus infections.BMC Biotechnol. 2003 Mar 20;3:3. doi: 10.1186/1472-6750-3-3. Epub 2003 Mar 20. BMC Biotechnol. 2003. PMID: 12659646 Free PMC article.
-
Double-stranded RNA binding may be a general plant RNA viral strategy to suppress RNA silencing.J Virol. 2006 Jun;80(12):5747-56. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01963-05. J Virol. 2006. PMID: 16731914 Free PMC article.
-
RNA interference as a new biotechnological tool for the control of virus diseases in plants.Virus Res. 2004 Jun 1;102(1):85-96. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2004.01.019. Virus Res. 2004. PMID: 15068884 Review.
-
Plant viral suppressors of RNA silencing.Virus Res. 2004 Jun 1;102(1):97-108. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2004.01.020. Virus Res. 2004. PMID: 15068885 Review.
Cited by
-
Detection of Plant Viruses and Disease Management: Relevance of Genetic Diversity and Evolution.Front Plant Sci. 2020 Jul 17;11:1092. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2020.01092. eCollection 2020. Front Plant Sci. 2020. PMID: 32765569 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exogenous Application of dsRNA in Plant Protection: Efficiency, Safety Concerns and Risk Assessment.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jun 13;25(12):6530. doi: 10.3390/ijms25126530. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38928236 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Topical Application of Double-Stranded RNA Targeting 2b and CP Genes of Cucumber mosaic virus Protects Plants against Local and Systemic Viral Infection.Plants (Basel). 2021 May 12;10(5):963. doi: 10.3390/plants10050963. Plants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34066062 Free PMC article.
-
Application of Exogenous dsRNAs-induced RNAi in Agriculture: Challenges and Triumphs.Front Plant Sci. 2020 Jun 25;11:946. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2020.00946. eCollection 2020. Front Plant Sci. 2020. PMID: 32670336 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exogenous Application of RNAi-Inducing Double-Stranded RNA Inhibits Aphid-Mediated Transmission of a Plant Virus.Front Plant Sci. 2019 Mar 15;10:265. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2019.00265. eCollection 2019. Front Plant Sci. 2019. PMID: 30930914 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alonso E, García-Luque I, De la Cruz A, Wicke B, Avila-Rincón M J, Serra M T, Castresana C, Díaz-Ruíz J R. Nucleotide sequence of the genomic RNA of pepper mild mottle virus, a resistance-breaking tobamovirus in pepper. J Gen Virol. 1991;72:2875–2884. - PubMed
-
- Bass B L. Double-stranded RNA as a template for gene silencing. Cell. 2000;101:235–238. - PubMed
-
- Bol J F. Alfalfa mosaic virus and ilarviruses: involvement of coat protein in multiple steps of the replication cycle. J Gen Virol. 1999;80:1089–1102. - PubMed
-
- Cogoni C, Macino G. Homology-dependent gene silencing in plants and fungi: a number of variations on the same theme. Curr Opin Microbiol. 1999;2:657–662. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

