Transcriptional consequences of topoisomerase inhibition
- PMID: 11713279
- PMCID: PMC100007
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.21.24.8437-8451.2001
Transcriptional consequences of topoisomerase inhibition
Abstract
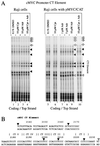
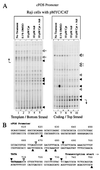
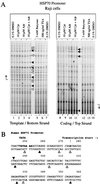
In principle, the generation, transmission, and dissipation of supercoiling forces are determined by the arrangement of the physical barriers defining topological boundaries and the disposition of enzymes creating (polymerases and helicases, etc.) or releasing (topoisomerases) torsional strain in DNA. These features are likely to be characteristic for individual genes. By using topoisomerase inhibitors to alter the balance between supercoiling forces in vivo, we monitored changes in the basal transcriptional activity and DNA conformation for several genes. Every gene examined displayed an individualized profile in response to inhibition of topoisomerase I or II. The expression changes elicited by camptothecin (topoisomerase I inhibitor) or adriamycin (topoisomerase II inhibitor) were not equivalent. Camptothecin generally caused transcription complexes to stall in the midst of transcription units, while provoking little response at promoters. Adriamycin, in contrast, caused dramatic changes at or near promoters and prevented transcription. The response to topoisomerase inhibition was also context dependent, differing between chromosomal or episomal c-myc promoters. In addition to being well-characterized DNA-damaging agents, topoisomerase inhibitors may evoke a biological response determined in part from transcriptional effects. The results have ramifications for the use of these drugs as antineoplastic agents.
Figures









References
-
- Aller P, Rius C, Mata F, Zorrilla A, Cabanas C, Bellon T, Bernabeu C. Camptothecin induces differentiation and stimulates the expression of differentiation-related genes in U-937 human promonocytic leukemia cells. Cancer Res. 1992;52:1245–1251. - PubMed
-
- Amara F M, Entwistle J, Kuschak T I, Turley E A, Wright J A. Transforming growth factor-β1 stimulates multiple protein interactions at a unique cis-element in the 3′-untranslated region of the hyaluronan receptor RHAMM mRNA. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:15279–15284. - PubMed
-
- Bates A D, Maxwell A. DNA Topology. Oxford, England: IRL Press; 1993.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
