p38 MAP kinase modulates liver cell volume through inhibition of membrane Na+ permeability
- PMID: 11714741
- PMCID: PMC209415
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI12190
p38 MAP kinase modulates liver cell volume through inhibition of membrane Na+ permeability
Abstract
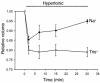
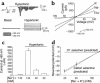
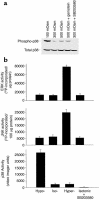
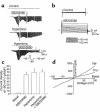
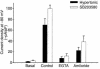
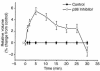
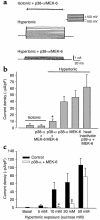
In hepatocytes, Na+ influx through nonselective cation (NSC) channels represents a key point for regulation of cell volume. Under basal conditions, channels are closed, but both physiologic and pathologic stimuli lead to a large increase in Na+ and water influx. Since osmotic stimuli also activate mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase pathways, we have examined regulation of Na+ permeability and cell volume by MAP kinases in an HTC liver cell model. Under isotonic conditions, there was constitutive activity of p38 MAP kinase that was selectively inhibited by SB203580. Decreases in cell volume caused by hypertonic exposure had no effect on p38, but increases in cell volume caused by hypotonic exposure increased p38 activity tenfold. Na+ currents were small when cells were in isotonic media but could be increased by inhibiting constitutive p38 MAP kinase, thereby increasing cell volume. To evaluate the potential inhibitory role of p38 more directly, cells were dialyzed with recombinant p38alpha and its upstream activator, MEK-6, which substantially inhibited volume-sensitive currents. These findings indicate that constitutive p38 activity contributes to the low Na+ permeability necessary for maintenance of cell volume, and that recombinant p38 negatively modulates the set point for volume-sensitive channel opening. Thus, functional interactions between p38 MAP kinase and ion channels may represent an important target for modifying volume-sensitive liver functions.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Volume-sensitive tyrosine kinases regulate liver cell volume through effects on vesicular trafficking and membrane Na+ permeability.J Biol Chem. 2003 Nov 7;278(45):44632-8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M301958200. Epub 2003 Aug 25. J Biol Chem. 2003. PMID: 12939281
-
Hypotonic shock mediation by p38 MAPK, JNK, PKC, FAK, OSR1 and SPAK in osmosensing chloride secreting cells of killifish opercular epithelium.J Exp Biol. 2005 Mar;208(Pt 6):1063-77. doi: 10.1242/jeb.01491. J Exp Biol. 2005. PMID: 15767308
-
Role of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase in lung injury after burn trauma.Shock. 2003 May;19(5):475-9. doi: 10.1097/01.shk.0000055242.25446.84. Shock. 2003. PMID: 12744493
-
Pyridinylimidazole based p38 MAP kinase inhibitors.Curr Top Med Chem. 2002 Sep;2(9):1011-20. doi: 10.2174/1568026023393372. Curr Top Med Chem. 2002. PMID: 12171568 Review.
-
Osmosensing and signaling in the regulation of liver function.Contrib Nephrol. 2006;152:198-209. doi: 10.1159/000096324. Contrib Nephrol. 2006. PMID: 17065813 Review.
Cited by
-
Modulation of h-channels in hippocampal pyramidal neurons by p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase.J Neurosci. 2006 Jul 26;26(30):7995-8003. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2069-06.2006. J Neurosci. 2006. PMID: 16870744 Free PMC article.
-
PKCα regulates TMEM16A-mediated Cl⁻ secretion in human biliary cells.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2016 Jan 1;310(1):G34-42. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00146.2015. Epub 2015 Nov 5. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2016. PMID: 26542395 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of mechanosensitive biliary epithelial transport by the epithelial Na(+) channel.Hepatology. 2016 Feb;63(2):538-49. doi: 10.1002/hep.28301. Epub 2015 Dec 14. Hepatology. 2016. PMID: 26475057 Free PMC article.
-
Fluid flow induces mechanosensitive ATP release, calcium signalling and Cl- transport in biliary epithelial cells through a PKCzeta-dependent pathway.J Physiol. 2008 Jun 1;586(11):2779-98. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2008.153015. Epub 2008 Apr 3. J Physiol. 2008. PMID: 18388137 Free PMC article.
-
Cell membrane alignment along adhesive surfaces: contribution of active and passive cell processes.Biophys J. 2003 Mar;84(3):2058-70. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(03)75013-9. Biophys J. 2003. PMID: 12609907 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Paul A, et al. Stress-activated protein kinases: activation, regulation and function. Cell Signal. 1997;9:403–410. - PubMed
-
- Bode JG, et al. The mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase p38 and its upstream activator MAP kinase kinase 6 are involved in the activation of signal transducer and activator of transcription by hyperosmolarity. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:30222–30227. - PubMed
-
- Han J, Richter B, Li Z, Kravchenko V, Ulevitch RJ. Molecular cloning of human p38 MAP kinase. . Biochim Biophys Acta. 1995; 1265:224–227. - PubMed
-
- Han J, Lee JD, Bibbs L, Ulevitch RJ. A MAP kinase targeted by endotoxin and hyperosmolarity in mammalian cells. Science. 1994;265:808–811. - PubMed
-
- Derijard B, et al. Independent human MAP-kinase signal transduction pathways defined by MEK and MKK isoforms [erratum 1995, 269(5220):17] Science. 1995;267:682–685. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

