Processing of Mycobacterium tuberculosis antigen 85B involves intraphagosomal formation of peptide-major histocompatibility complex II complexes and is inhibited by live bacilli that decrease phagosome maturation
- PMID: 11714749
- PMCID: PMC2193679
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.194.10.1421
Processing of Mycobacterium tuberculosis antigen 85B involves intraphagosomal formation of peptide-major histocompatibility complex II complexes and is inhibited by live bacilli that decrease phagosome maturation
Abstract
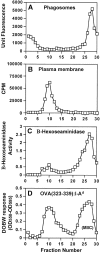
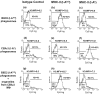
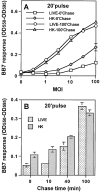
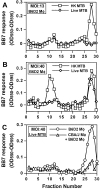
Mycobacterium tuberculosis (MTB) inhibits phagosomal maturation to promote its survival inside macrophages. Control of MTB infection requires CD4 T cell responses and major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class II (MHC-II) processing of MTB antigens (Ags). To investigate phagosomal processing of MTB Ags, phagosomes containing heat-killed (HK) or live MTB were purified from interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma)-activated macrophages by differential centrifugation and Percoll density gradient subcellular fractionation. Flow organellometry and Western blot analysis showed that MTB phagosomes acquired lysosome-associated membrane protein-1 (LAMP-1), MHC-II, and H2-DM. T hybridoma cells were used to detect MTB Ag 85B(241-256)-I-A(b) complexes in isolated phagosomes and other subcellular fractions. These complexes appeared initially (within 20 min) in phagosomes and subsequently (>20 min) on the plasma membrane, but never within late endocytic compartments. Macrophages processed HK MTB more rapidly and efficiently than live MTB; phagosomes containing live MTB expressed fewer Ag 85B(241-256)-I-A(b) complexes than phagosomes containing HK MTB. This is the first study of bacterial Ag processing to directly show that peptide-MHC-II complexes are formed within phagosomes and not after export of bacterial Ags from phagosomes to endocytic Ag processing compartments. Live MTB can alter phagosome maturation and decrease MHC-II Ag processing, providing a mechanism for MTB to evade immune surveillance and enhance its survival within the host.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Phagosomal processing of Mycobacterium tuberculosis antigen 85B is modulated independently of mycobacterial viability and phagosome maturation.Infect Immun. 2005 Feb;73(2):1097-105. doi: 10.1128/IAI.73.2.1097-1105.2005. Infect Immun. 2005. PMID: 15664953 Free PMC article.
-
Role of phagosomes and major histocompatibility complex class II (MHC-II) compartment in MHC-II antigen processing of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in human macrophages.Infect Immun. 2006 Mar;74(3):1621-30. doi: 10.1128/IAI.74.3.1621-1630.2006. Infect Immun. 2006. PMID: 16495533 Free PMC article.
-
Phagosomes are fully competent antigen-processing organelles that mediate the formation of peptide:class II MHC complexes.J Immunol. 1999 Mar 15;162(6):3263-72. J Immunol. 1999. PMID: 10092778
-
Phagocytic processing of antigens for presentation by class II major histocompatibility complex molecules.Cell Microbiol. 1999 Nov;1(3):205-14. doi: 10.1046/j.1462-5822.1999.00026.x. Cell Microbiol. 1999. PMID: 11207553 Review.
-
Phagocytic antigen processing and effects of microbial products on antigen processing and T-cell responses.Immunol Rev. 1999 Apr;168:217-39. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1999.tb01295.x. Immunol Rev. 1999. PMID: 10399077 Review.
Cited by
-
The ΔfbpAΔsapM candidate vaccine derived from Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Rv is markedly immunogenic in macrophages and induces robust immunity to tuberculosis in mice.Front Immunol. 2024 Jun 21;15:1321657. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1321657. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38975346 Free PMC article.
-
A recombinant bovine adenoviral mucosal vaccine expressing mycobacterial antigen-85B generates robust protection against tuberculosis in mice.Cell Rep Med. 2021 Aug 17;2(8):100372. doi: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2021.100372. eCollection 2021 Aug 17. Cell Rep Med. 2021. PMID: 34467249 Free PMC article.
-
Current efforts and future prospects in the development of live mycobacteria as vaccines.Expert Rev Vaccines. 2015;14(11):1493-507. doi: 10.1586/14760584.2015.1089175. Epub 2015 Sep 14. Expert Rev Vaccines. 2015. PMID: 26366616 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A mutant of Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Rv that lacks expression of antigen 85A is attenuated in mice but retains vaccinogenic potential.Infect Immun. 2004 Dec;72(12):7084-95. doi: 10.1128/IAI.72.12.7084-7095.2004. Infect Immun. 2004. PMID: 15557632 Free PMC article.
-
The Mycobacterium tuberculosis phagosome is a HLA-I processing competent organelle.PLoS Pathog. 2009 Apr;5(4):e1000374. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1000374. Epub 2009 Apr 10. PLoS Pathog. 2009. PMID: 19360129 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barnes, P.F., S.D. Mistry, C.L. Cooper, C. Pirmez, T.H. Rea, and R.L. Modlin. 1989. Compartmentalization of a CD4+ T lymphocyte subpopulation in tuberculous pleuritis. J. Immunol. 142:1114–1119. - PubMed
-
- Barnes, P.F., A.B. Bloch, P.T. Davidson, and D.E. Snider, Jr. 1991. Tuberculosis in patients with human immunodeficiency virus infection. N. Engl. J. Med. 324:1644–1650. - PubMed
-
- Tsukaguchi, K., K.N. Balaji, and W.H. Boom. 1995. CD4+ alpha-beta T cell and gamma delta T cell reponses to Mycobacterium tuberculosis: similarities and differences in antigen recognition, cytotoxic effector function, and cytokine production. J. Immunol. 154:1786–1796. - PubMed
-
- Pancholi, P., A. Mirza, N. Bhardwaj, and R.M. Steinman. 1993. Sequestration from immune CD4+ T cells of mycobacteria growing in human macrophages. Science. 260:984–986. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

