Acquisition of external major histocompatibility complex class I molecules by natural killer cells expressing inhibitory Ly49 receptors
- PMID: 11714758
- PMCID: PMC2193673
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.194.10.1519
Acquisition of external major histocompatibility complex class I molecules by natural killer cells expressing inhibitory Ly49 receptors
Erratum in
- J Exp Med 2001 Dec 17;194(12):1885
Abstract
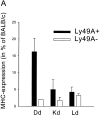
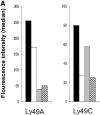
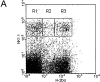
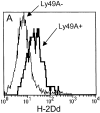
Murine natural killer (NK) cells express inhibitory Ly49 receptors specific for major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I molecules. We report that during interactions with cells in the environment, NK cells acquired MHC class I ligands from surrounding cells in a Ly49-specific fashion and displayed them at the cell surface. Ligand acquisition sometimes reached 20% of the MHC class I expression on surrounding cells, involved transfer of the entire MHC class I protein to the NK cell, and was independent of whether or not the NK cell expressed the MHC class I ligand itself. We also present indirect evidence for spontaneous MHC class I acquisition in vivo, as well as describe an in vitro coculture system with transfected cells in which the same phenomenon occurred. Functional studies in the latter model showed that uptake of H-2D(d) by Ly49A+ NK cells was accompanied by a partial inactivation of cytotoxic activity in the NK cell, as tested against H-2D(d)-negative target cells. In addition, ligand acquisition did not abrogate the ability of Ly49A+ NK cells to receive inhibitory signals from external H-2D(d) molecules. This study is the first to describe ligand acquisition by NK cells, which parallels recently described phenomena in T and B cells.
Figures










Similar articles
-
MHC class I recognition by NK receptors in the Ly49 family is strongly influenced by the beta 2-microglobulin subunit.J Immunol. 2001 Jun 15;166(12):7327-34. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.166.12.7327. J Immunol. 2001. PMID: 11390483
-
External and internal calibration of the MHC class I-specific receptor Ly49A on murine natural killer cells.J Immunol. 1998 Dec 1;161(11):6133-8. J Immunol. 1998. PMID: 9834098
-
The functional binding site for the C-type lectin-like natural killer cell receptor Ly49A spans three domains of its major histocompatibility complex class I ligand.J Exp Med. 2001 Jan 15;193(2):147-58. doi: 10.1084/jem.193.2.147. J Exp Med. 2001. PMID: 11148219 Free PMC article.
-
Structural basis of MHC class I recognition by natural killer cell receptors.Immunol Rev. 2001 Jun;181:52-65. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-065x.2001.1810104.x. Immunol Rev. 2001. PMID: 11513152 Review.
-
MHC class I recognition by Ly49 natural killer cell receptors.Mol Immunol. 2002 May;38(14):1023-7. doi: 10.1016/s0161-5890(02)00031-7. Mol Immunol. 2002. PMID: 11955594 Review.
Cited by
-
Adaptations of Natural Killer Cells to Self-MHC Class I.Front Immunol. 2014 Jul 22;5:349. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2014.00349. eCollection 2014. Front Immunol. 2014. PMID: 25101089 Free PMC article.
-
Transfer of NKG2D and MICB at the cytotoxic NK cell immune synapse correlates with a reduction in NK cell cytotoxic function.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006 Jul 25;103(30):11258-63. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0600721103. Epub 2006 Jul 18. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006. PMID: 16849432 Free PMC article.
-
MHC class I-deficient natural killer cells acquire a licensed phenotype after transfer into an MHC class I-sufficient environment.J Exp Med. 2010 Sep 27;207(10):2073-9. doi: 10.1084/jem.20100986. Epub 2010 Sep 6. J Exp Med. 2010. PMID: 20819924 Free PMC article.
-
Intercellular transfer of MHC and immunological molecules: molecular mechanisms and biological significance.Am J Transplant. 2007 Jun;7(6):1442-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-6143.2007.01816.x. Am J Transplant. 2007. PMID: 17511673 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Glycosylation contributes to variability in expression of murine cytomegalovirus m157 and enhances stability of interaction with the NK-cell receptor Ly49H.Eur J Immunol. 2010 Sep;40(9):2618-31. doi: 10.1002/eji.200940134. Eur J Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20662096 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yokoyama, W.M. 1999. Natural Killer Cells. 4th edition. Fundamental Immunology. P. Ewe, editor. Lippincott-Raven, Philadelphia. 575–603 pp.
-
- Lanier, L.L. 1998. NK cell receptors. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 16:359–393. - PubMed
-
- Ljunggren, H.G., and K. Kärre. 1990. In search of the ‘missing self’: MHC molecules and NK cell recognition. Immunol. Today. 11:237–244. - PubMed
-
- Karlhofer, F.M., R.K. Ribaudo, and W.M. Yokoyama. 1992. MHC class I alloantigen specificity of Ly-49+ IL-2-activated natural killer cells. Nature. 358:66–70. - PubMed
-
- Grakoui, A., S.K. Bromley, C. Sumen, M.M. Davis, A.S. Shaw, P.M. Allen, and M.L. Dustin. 1999. The immunological synapse: a molecular machine controlling T cell activation. Science. 285:221–227. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

