Structure and dynamics of translation initiation factor aIF-1A from the archaeon Methanococcus jannaschii determined by NMR spectroscopy
- PMID: 11714910
- PMCID: PMC2374032
- DOI: 10.1110/ps.18201
Structure and dynamics of translation initiation factor aIF-1A from the archaeon Methanococcus jannaschii determined by NMR spectroscopy
Abstract
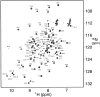
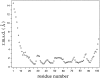
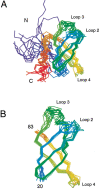
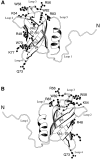
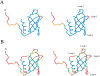
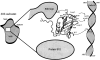
Translation initiation factor 1A (aIF-1A) from the archaeon Methanococcus jannaschii was expressed in Escherichia coli, purified, and characterized in terms of its structure and dynamics using multidimensional NMR methods. The protein was found to be a member of the OB-fold family of RNA-associated proteins, containing a barrel of five beta-strands, a feature that is shared with the homologous eukaryotic translation initiation factor 1A (eIF-1A), as well as the prokaryotic translation initiation factor IF1. External to the beta barrel, aIF-1A contains an alpha-helix at its C-terminal and a flexible loop at its N-terminal, features that are qualitatively similar to those found in eIF-1A, but not present in prokaryotic IF1. The structural model of aIF-1A, when used in combination with primary sequence information for aIF-1A in divergent species, permitted the most-conserved residues on the protein surface to be identified, including the most likely candidates for direct interaction with the 16S ribosomal RNA and other components of the translational apparatus. Several of the conserved surface residues appear to be unique to the archaea. Nitrogen-15 relaxation and amide exchange rate data were used to characterize the internal motions within aIF-1A, providing evidence that the protein surfaces that are most likely to participate in intermolecular interactions are relatively flexible. A model is proposed, suggesting some specific interactions that may occur between aIF-1A and the small subunit of the archaeal ribosome.
Figures

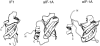
Similar articles
-
Structure of the beta subunit of translation initiation factor 2 from the archaeon Methanococcus jannaschii: a representative of the eIF2beta/eIF5 family of proteins.Biochemistry. 2002 May 7;41(18):5730-42. doi: 10.1021/bi011984n. Biochemistry. 2002. PMID: 11980477
-
The structure of the translational initiation factor IF1 from E.coli contains an oligomer-binding motif.EMBO J. 1997 Mar 17;16(6):1436-43. doi: 10.1093/emboj/16.6.1436. EMBO J. 1997. PMID: 9135158 Free PMC article.
-
Crystal structures of ribosome anti-association factor IF6.Nat Struct Biol. 2000 Dec;7(12):1156-64. doi: 10.1038/82017. Nat Struct Biol. 2000. PMID: 11101899
-
Structure of a two-domain N-terminal fragment of ribosomal protein L10 from Methanococcus jannaschii reveals a specific piece of the archaeal ribosomal stalk.J Mol Biol. 2010 Jun 4;399(2):214-20. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2010.04.017. Epub 2010 Apr 24. J Mol Biol. 2010. PMID: 20399793 Review.
-
Translation initiation in Archaea: conserved and domain-specific features.Biochem Soc Trans. 2011 Jan;39(1):89-93. doi: 10.1042/BST0390089. Biochem Soc Trans. 2011. PMID: 21265752 Review.
Cited by
-
NABP1, a novel RORgamma-regulated gene encoding a single-stranded nucleic-acid-binding protein.Biochem J. 2006 Jul 1;397(1):89-99. doi: 10.1042/BJ20051781. Biochem J. 2006. PMID: 16533169 Free PMC article.
-
Nucleic acid recognition by OB-fold proteins.Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct. 2003;32:115-33. doi: 10.1146/annurev.biophys.32.110601.142506. Epub 2003 Feb 18. Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct. 2003. PMID: 12598368 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The origins and evolution of translation factors.Trends Genet. 2025 Jul;41(7):590-600. doi: 10.1016/j.tig.2025.02.004. Epub 2025 Mar 24. Trends Genet. 2025. PMID: 40133153 Review.
-
Relative stabilities of conserved and non-conserved structures in the OB-fold superfamily.Int J Mol Sci. 2009 May 22;10(5):2412-2430. doi: 10.3390/ijms10052412. Int J Mol Sci. 2009. PMID: 19564956 Free PMC article.
-
Structure of Mth11/Mth Rpp29, an essential protein subunit of archaeal and eukaryotic RNase P.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003 Dec 23;100(26):15398-403. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2535887100. Epub 2003 Dec 12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003. PMID: 14673079 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ban, N., Nissen, P., Hansen, J., Moore, P.B., and Steitz, T.A. 2000. The complete atomic structure of the large ribosomal subunit at 2.4 Å resolution. Science 289 905–920. - PubMed
-
- Battiste, J.L., Pestova, T.V., Hellen, C.U., and Wagner, G. 2000. The eIF1A solution structure reveals a large RNA-binding surface important for scanning function. Mol. Cell 5 109–119. - PubMed
-
- Bell, S.D. and Jackson, S.P. 1998. Transcription and translation in Archaea: A mosaic of eukaryal and bacterial features. Trends Microbiol. 6 222–228. - PubMed
-
- Brock, S., Szkaradkiewicz, K., and Sprinzl, M. 1998. Initiation factors of protein biosynthesis in bacteria and their structural relationship to the elongation and termination factors. Mol. Microbiol. 29 409–417. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

