Motif-based fold assignment
- PMID: 11714913
- PMCID: PMC2374048
- DOI: 10.1110/ps.14401
Motif-based fold assignment
Abstract
Conventional fold recognition techniques rely mainly on the analysis of the entire sequence of a protein. We present an MBA method to improve performance of any conventional sequence-based fold assignment. The method uses sequence motifs, such as those defined in the Prosite database, and the SwissProt annotation of the fold library. When combined with a simple SDP method, the coverage of MBA is comparable to the results obtained with PSI-BLAST. However, the set of the MBA predictions is significantly different from that of PSI-BLAST, leading to a 40% increase of the coverage for the combined MBA/PSI-BLAST method. The MBA approach can be easily adopted to include the results of sequence-independent function prediction methods and alternative motif and annotation databases. The method is available through the web server localized at http://www.doe-mbi.ucla.edu/mba.
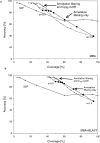
Figures
Similar articles
-
Scan2S: increasing the precision of PROSITE pattern motifs using secondary structure constraints.Proteins. 2008 Sep;72(4):1138-47. doi: 10.1002/prot.22008. Proteins. 2008. PMID: 18320586
-
Fast model-based protein homology detection without alignment.Bioinformatics. 2007 Jul 15;23(14):1728-36. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btm247. Epub 2007 May 8. Bioinformatics. 2007. PMID: 17488755
-
Exploring the extremes of sequence/structure space with ensemble fold recognition in the program Phyre.Proteins. 2008 Feb 15;70(3):611-25. doi: 10.1002/prot.21688. Proteins. 2008. PMID: 17876813
-
Predicting functional sites with an automated algorithm suitable for heterogeneous datasets.BMC Bioinformatics. 2005 May 13;6:116. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-6-116. BMC Bioinformatics. 2005. PMID: 15890082 Free PMC article.
-
Structural genomics: computational methods for structure analysis.Protein Sci. 2003 Sep;12(9):1813-21. doi: 10.1110/ps.0242903. Protein Sci. 2003. PMID: 12930981 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
DescFold: a web server for protein fold recognition.BMC Bioinformatics. 2009 Dec 14;10:416. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-10-416. BMC Bioinformatics. 2009. PMID: 20003426 Free PMC article.
-
Descriptor-based protein remote homology identification.Protein Sci. 2005 Feb;14(2):431-44. doi: 10.1110/ps.041035505. Epub 2005 Jan 4. Protein Sci. 2005. PMID: 15632283 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of GATC- and CCGG-recognizing Type II REases and their putative specificity-determining positions using Scan2S--a novel motif scan algorithm with optional secondary structure constraints.Proteins. 2008 May 1;71(2):631-40. doi: 10.1002/prot.21777. Proteins. 2008. PMID: 17972284 Free PMC article.
-
The directional atomic solvation energy: an atom-based potential for the assignment of protein sequences to known folds.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002 Dec 10;99(25):16041-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.252626399. Epub 2002 Dec 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002. PMID: 12461172 Free PMC article.
-
TIM-Finder: a new method for identifying TIM-barrel proteins.BMC Struct Biol. 2009 Dec 14;9:73. doi: 10.1186/1472-6807-9-73. BMC Struct Biol. 2009. PMID: 20003393 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Andrade, M., Casari, G., de Daruvar, A., Sander, C., Schneider, R., Tamames, J., Valencia, A., and Ouzounis, C. 1997. Sequence analysis of the Methanococcus jannaschii genome and the prediction of protein function. Comput. Appl. Biosci. 13 481–483. - PubMed
-
- Andrade, M.A., Brown, N.P., Leroy, C., Hoersch, S., de Daruvar, A., Reich, C., Franchini, A., Tamames, J., Valencia, A., Ouzounis, C., and Sander, C. 1999. Automated genome sequence analysis and annotation. Bioinformatics 15 391–412. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

