P2X2 receptor mediates stimulation of parasensory cation absorption by cochlear outer sulcus cells and vestibular transitional cells
- PMID: 11717350
- PMCID: PMC6763907
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.21-23-09168.2001
P2X2 receptor mediates stimulation of parasensory cation absorption by cochlear outer sulcus cells and vestibular transitional cells
Abstract
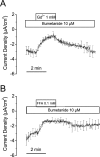
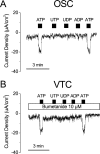
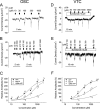
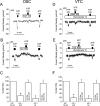
Cochlear outer sulcus cells (OSC) and vestibular transitional cells (VTC) are part of the parasensory epithelium in the inner ear and are located in homologous positions between the sensory hair cells and the cation secretory epithelial cells in the cochlea and the vestibular labyrinth. OSC are known to sustain a reabsorptive transepithelial current and to contain an immunoreactivity for P2X(2) purinergic receptors. This study addresses whether OSC and VTC share functional similarities and extends this hypothesis to the question of whether both cell types contain functional P2X(2) receptors. The current density (I(sc)) was recorded with the vibrating probe technique and was found to be similar in VTC and OSC. Both gadolinium and flufenamic acid reduced I(sc) in VTC, as reported previously for OSC. I(sc) was stimulated by extracellular ATP but not by selective agonists of P2Y receptors. Purinergic receptor agonists increased I(sc) with a potency order of ATP > 2'- and 3'-O-(4-benzoyl-benzoyl)adenosine 5'-triphosphate alpha,beta-methyleneadenosine 5'-triphosphate in both OSC and VTC. In the presence of suramin (100 micrometer) or gadolinium (100 micrometer), the responses of ATP were inhibited significantly in both OSC and VTC. This pharmacological profile is consistent with that of the P2X(2) receptor. These results demonstrate that VTC participate in vestibular parasensory cation absorption and that both OSC and VTC regulate their parasensory cation flux via P2X(2) receptors, which would regulate the endolymphatic concentration of the current-carrying ion species in auditory and vestibular transduction.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Changes in P2Y4 receptor expression in rat cochlear outer sulcus cells during development.Hear Res. 2007 Jun;228(1-2):201-11. doi: 10.1016/j.heares.2007.02.008. Epub 2007 Mar 2. Hear Res. 2007. PMID: 17433586
-
ATP-gated ion channels assembled from P2X2 receptor subunits in the mouse cochlea.Neuroreport. 2002 Oct 28;13(15):1979-84. doi: 10.1097/00001756-200210280-00030. Neuroreport. 2002. PMID: 12395104
-
Characterization of cultured dorsal root ganglion neuron P2X receptors.Eur J Neurosci. 1999 Jan;11(1):149-54. doi: 10.1046/j.1460-9568.1999.00426.x. Eur J Neurosci. 1999. PMID: 9987019
-
Functional properties of native and cloned P2X receptors.Ciba Found Symp. 1996;198:208-19; discussion 219-22. doi: 10.1002/9780470514900.ch12. Ciba Found Symp. 1996. PMID: 8879827 Review.
-
Regulation of sodium transport in the inner ear.Hear Res. 2011 Oct;280(1-2):21-9. doi: 10.1016/j.heares.2011.05.003. Epub 2011 May 18. Hear Res. 2011. PMID: 21620939 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
ATP-mediated potassium recycling in the cochlear supporting cells.Purinergic Signal. 2010 Jun;6(2):221-9. doi: 10.1007/s11302-010-9184-9. Epub 2010 May 18. Purinergic Signal. 2010. PMID: 20806014 Free PMC article.
-
Temporal and spatial distribution of gentamicin in the peripheral vestibular system after transtympanic administration in guinea pigs.Hear Res. 2013 Apr;298:49-59. doi: 10.1016/j.heares.2013.01.010. Epub 2013 Feb 1. Hear Res. 2013. PMID: 23380663 Free PMC article.
-
Water permeability of the mammalian cochlea: functional features of an aquaporin-facilitated water shunt at the perilymph-endolymph barrier.Pflugers Arch. 2014 Oct;466(10):1963-85. doi: 10.1007/s00424-013-1421-y. Epub 2014 Jan 3. Pflugers Arch. 2014. PMID: 24385019 Free PMC article.
-
Differential Effects of Hearing Loss Mutations in Homomeric P2X2 and Heteromeric P2X2/3 Receptors.Cells. 2025 Mar 29;14(7):510. doi: 10.3390/cells14070510. Cells. 2025. PMID: 40214464 Free PMC article.
-
Hair cells--beyond the transducer.J Membr Biol. 2006 Feb-Mar;209(2-3):89-118. doi: 10.1007/s00232-005-0835-7. Epub 2006 May 25. J Membr Biol. 2006. PMID: 16773496 Review.
References
-
- Brandle U, Zenner HP, Ruppersberg JP. Gene expression of P2X-receptors in the developing inner ear of the rat. Neurosci Lett. 1999;273:105–108. - PubMed
-
- Chiba T, Marcus DC. Nonselective cation and BK channels in apical membrane of outer sulcus epithelial cells. J Membr Biol. 2000;174:167–179. - PubMed
-
- Chiba T, Marcus DC. Basolateral K+ conductance establishes driving force for cation absorption by outer sulcus epithelial cells. J Membr Biol. 2001;184:101–112. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
