Roles of the telencephalic cells and their chondroitin sulfate proteoglycans in delimiting an anterior border of the retinal pathway
- PMID: 11717364
- PMCID: PMC6763928
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.21-23-09304.2001
Roles of the telencephalic cells and their chondroitin sulfate proteoglycans in delimiting an anterior border of the retinal pathway
Abstract
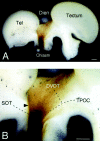
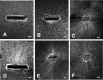
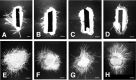
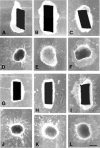
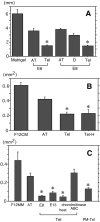
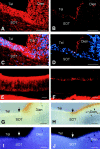
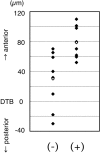
The axons of the retinal ganglion cells run on the diencephalotelencephalic boundary on their way to the tectum; however, they do not invade the telencephalon anteriorly. To investigate the mechanisms that prevent the retinal axons from entering the telencephalic territory, the effects of the telencephalic cells were examined on the outgrowth of the retinal axons in vitro; the retinal outgrowth was selectively inhibited by the cellular substrate derived from the telencephalon. The responsible factor for the selective inhibition was, furthermore, found in the telencephalic membranes and the fraction of peripheral membrane molecules from the telencephalon. Because the inhibitory effect was destroyed by chondroitinase ABC but not by heat, this inhibition was attributable to the carbohydrate chains of chondroitin sulfate proteoglycans (CSPGs) adhering to the membranes of the telencephalic cells. To understand the function of the telencephalic CSPGs on the retinal pathfinding in vivo, their carbohydrate chains [chondroitin sulfate glycosaminoglycan (CS-GAG)] were removed from the embryonic brains by intraventricular injection of chondroitinase ABC; the removal of CS-GAG resulted in an anterior enlargement of the optic tract. The results indicate that the telencephalic cells delimit the anterior border of the optic tract with their CSPGs and prevent the retinal axons from aberrantly entering the anterior territory.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Limited growth of severed CNS axons after treatment of adult rat brain with hyaluronidase.J Neurosci Res. 2003 Jan 1;71(1):23-37. doi: 10.1002/jnr.10449. J Neurosci Res. 2003. PMID: 12478611
-
Repellent guidance of regenerating optic axons by chondroitin sulfate glycosaminoglycans in zebrafish.J Neurosci. 2002 Feb 1;22(3):842-53. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.22-03-00842.2002. J Neurosci. 2002. PMID: 11826114 Free PMC article.
-
Restricted distribution of D-unit-rich chondroitin sulfate carbohydrate chains in the neuropil encircling the optic tract and on a subset of retinal axons in chick embryos.J Comp Neurol. 2006 Apr 1;495(4):470-9. doi: 10.1002/cne.20892. J Comp Neurol. 2006. PMID: 16485291
-
Structural variation of chondroitin sulfate and its roles in the central nervous system.Cent Nerv Syst Agents Med Chem. 2010 Mar;10(1):22-31. doi: 10.2174/187152410790780136. Cent Nerv Syst Agents Med Chem. 2010. PMID: 20236040 Review.
-
Overcoming chondroitin sulphate proteoglycan inhibition of axon growth in the injured brain: lessons from chondroitinase ABC.Curr Pharm Des. 2007;13(24):2485-92. doi: 10.2174/138161207781368639. Curr Pharm Des. 2007. PMID: 17692016 Review.
Cited by
-
Postnatal lethality and chondrodysplasia in mice lacking both chondroitin sulfate N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase-1 and -2.PLoS One. 2017 Dec 29;12(12):e0190333. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0190333. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 29287114 Free PMC article.
-
Glycans and Carbohydrate-Binding/Transforming Proteins in Axon Physiology.Adv Neurobiol. 2023;29:185-217. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-12390-0_7. Adv Neurobiol. 2023. PMID: 36255676
-
Glycosylation in Axonal Guidance.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 May 13;22(10):5143. doi: 10.3390/ijms22105143. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34068002 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chemistry and Function of Glycosaminoglycans in the Nervous System.Adv Neurobiol. 2023;29:117-162. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-12390-0_5. Adv Neurobiol. 2023. PMID: 36255674 Review.
-
Respiratory dysfunction following neonatal sustained hypoxia exposure during a critical window of brain stem extracellular matrix formation.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2018 Feb 1;314(2):R216-R227. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00199.2017. Epub 2017 Oct 18. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29046314 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anderson RB, Key B. Novel guidance cues during neuronal pathfinding in the early scaffold of axon tracts in the rostral brain. Development. 1999;126:1859–1868. - PubMed
-
- Anderson RB, Walz A, Holt CE, Key B. Chondroitin sulfates modulate axon guidance in embryonic Xenopus brain. Dev Biol. 1998;202:235–243. - PubMed
-
- Brittis PA, Canning DR, Silver J. Chondroitin sulfate as a regulator of neuronal patterning in the retina. Science. 1992;255:733–736. - PubMed
-
- Brusca JS, Radolf JD. Isolation of integral membrane proteins by phase partitioning with Triton X-114. Methods Enzymol. 1994;228:182–193. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
