Atrogin-1, a muscle-specific F-box protein highly expressed during muscle atrophy
- PMID: 11717410
- PMCID: PMC64700
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.251541198
Atrogin-1, a muscle-specific F-box protein highly expressed during muscle atrophy
Abstract
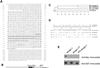
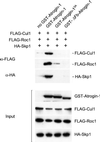
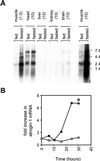
Muscle wasting is a debilitating consequence of fasting, inactivity, cancer, and other systemic diseases that results primarily from accelerated protein degradation by the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway. To identify key factors in this process, we have used cDNA microarrays to compare normal and atrophying muscles and found a unique gene fragment that is induced more than ninefold in muscles of fasted mice. We cloned this gene, which is expressed specifically in striated muscles. Because this mRNA also markedly increases in muscles atrophying because of diabetes, cancer, and renal failure, we named it atrogin-1. It contains a functional F-box domain that binds to Skp1 and thereby to Roc1 and Cul1, the other components of SCF-type Ub-protein ligases (E3s), as well as a nuclear localization sequence and PDZ-binding domain. On fasting, atrogin-1 mRNA levels increase specifically in skeletal muscle and before atrophy occurs. Atrogin-1 is one of the few examples of an F-box protein or Ub-protein ligase (E3) expressed in a tissue-specific manner and appears to be a critical component in the enhanced proteolysis leading to muscle atrophy in diverse diseases.
Figures

References
-
- Kettelhut I C, Wing S S, Goldberg A L. Diabetes Metab Rev. 1988;4:751–772. - PubMed
-
- Lecker S H, Solomon V, Mitch W E, Goldberg A L. J Nutr. 1999;129:227S–237S. - PubMed
-
- Mitch W E, Goldberg A L. N Engl J Med. 1996;335:1897–1905. - PubMed
-
- Jaspers S R, Tischler M E. J Appl Physiol. 1984;57:1472–1479. - PubMed
-
- Tischler M E, Rosenberg S, Satarug S, Henriksen E J, Kirby C R, Tome M, Chase P. Metabolism. 1990;39:756–763. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

