Flagellin stimulation of intestinal epithelial cells triggers CCL20-mediated migration of dendritic cells
- PMID: 11717433
- PMCID: PMC61108
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.241308598
Flagellin stimulation of intestinal epithelial cells triggers CCL20-mediated migration of dendritic cells
Abstract
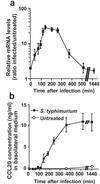
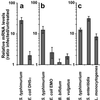
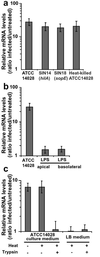
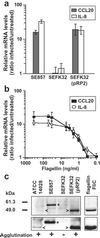
Enteropathogenic bacteria elicit mucosal innate and adaptive immune responses. We investigated whether gut epithelial cells played a role in triggering an adaptive immune response by recruiting dendritic cells (DCs). Immature DCs are selectively attracted by the CCL20 chemokine. The expression of the CCL20 gene in human intestinal epithelial cell lines was up-regulated by pathogenic bacteria, including Salmonella species, but not by indigenous bacteria of the intestinal flora. The Salmonella machinery for epithelial cell invasion was not required for CCL20 gene activation. Flagellin but not the lipopolysaccharide was found to be the Salmonella factor responsible for stimulation of epithelial CCL20 production. CCL20 in turn triggered a specific migration of immature DCs. Our data show that crosstalk between bacterial flagellin and epithelial cells is essential for the recruitment of DCs, a mechanism that could be instrumental to initiate adaptive immune responses in the gut.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Characterization of CCL20 secretion by human epithelial vaginal cells: involvement in Langerhans cell precursor attraction.J Leukoc Biol. 2005 Jul;78(1):158-66. doi: 10.1189/jlb.0305147. Epub 2005 Apr 14. J Leukoc Biol. 2005. PMID: 15831560
-
CCR6 and CCL20: partners in intestinal immunity and lymphorganogenesis.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2006 Aug;1072:52-61. doi: 10.1196/annals.1326.036. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2006. PMID: 17057190 Review.
-
Iron chelator induces MIP-alpha/CCL20 in human intestinal epithelial cells: implication for triggering mucosal adaptive immunity.Exp Mol Med. 2005 Aug 31;37(4):297-310. doi: 10.1038/emm.2005.40. Exp Mol Med. 2005. PMID: 16155407
-
Airway epithelial cells release MIP-3alpha/CCL20 in response to cytokines and ambient particulate matter.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2003 Jun;28(6):648-54. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2002-0095OC. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2003. PMID: 12760962
-
The airway epithelium as immune modulator: the LARC ascending.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2003 Jun;28(6):641-4. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.F271. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2003. PMID: 12760960 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Harnessing Colon Chip Technology to Identify Commensal Bacteria That Promote Host Tolerance to Infection.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021 Mar 12;11:638014. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2021.638014. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33777849 Free PMC article.
-
Flagellin of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli stimulates interleukin-8 production in T84 cells.Infect Immun. 2003 Apr;71(4):2120-9. doi: 10.1128/IAI.71.4.2120-2129.2003. Infect Immun. 2003. PMID: 12654834 Free PMC article.
-
Intestinal glucose uptake protects liver from lipopolysaccharide and D-galactosamine, acetaminophen, and alpha-amanitin in mice.Am J Pathol. 2009 Sep;175(3):1066-76. doi: 10.2353/ajpath.2009.090071. Epub 2009 Aug 21. Am J Pathol. 2009. PMID: 19700751 Free PMC article.
-
9,10-dihydro-2,5-dimethoxyphenanthrene-1,7-diol, from Eulophia ochreata, inhibits inflammatory signalling mediated by Toll-like receptors.Br J Pharmacol. 2010 Jul;160(5):1158-70. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2010.00780.x. Br J Pharmacol. 2010. PMID: 20590609 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced probiotic potential of Lactobacillus kefiranofaciens OSU-BDGOA1 through co-culture with Kluyveromyces marxianus bdgo-ym6.Front Microbiol. 2023 Aug 3;14:1236634. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1236634. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37601389 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

