Borderless teleradiology with CHILI
- PMID: 11720917
- PMCID: PMC1761707
- DOI: 10.2196/jmir.1.2.e8
Borderless teleradiology with CHILI
Abstract
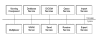
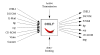
Teleradiology is one of the most evolved areas of telemedicine, but one of the basic problems which remains unsolved concerns system compatibility. The DICOM (Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine) standard is a prerequisite, but it is not sufficient in all aspects. Examples of other currently open issues are security and cooperative work in synchronous teleconferences. Users without a DICOM radiological workstation would benefit from the ability to join a teleradiology network without any special tools. Drawbacks of many teleradiology systems are that they are monolithic in their software design and cannot be adapted to the actual user's environment. Existing radiological systems currently cannot be extended with additional software components. Consequently, every new application usually needs a new workstation with a different look and feel, which must be connected and integrated into the existing infrastructure. This paper introduces the second generation teleradiology system CHILI. The system has been designed to match both the teleradiology requirements of the American College of Radiology (ACR), and the functionality and usability needs of the users. The experiences of software developers and teleradiology users who participated in the first years of the clinical use of CHILI's predecessor MEDICUS have been integrated into a new design. The system has been designed as a component-based architecture. The most powerful communication protocol for data exchange and teleconferencing is the CHILI protocol, which includes a strong data security concept. The system offers, in addition to its own secure protocol, several different communication Methods: DICOM, classic e-mail, Remote Copy functions (RCP), File Transfer Protocol (FTP), the internet protocols HTTP (HyperText Transfer Protocol) and HTTPS (HyperText Transfer Protocol Secure),and CD-ROMs for off-line communication. These transfer METHODS allow the user to send images to nearly anyone with a computer and a network. The drawbacks of the non-CHILI protocols are that teleconferences are not possible, and that the user must take reasonable precautions for data privacy and security. The CHILI PlugIn mechanism enables the users or third parties to extend the system capabilities by adding powerful image postprocessing functions or interfaces to other information systems. Suitable PlugIns can be either existing programs, or dedicated applications programmed with interfaces to the CHILI components. The developer may freely choose programming languages and interface toolkits. The CHILI architecture is a powerful and flexible environment for Picture Archiving and Communications Systems (PACS)and teleradiology. More than 40 systems are currently running in clinical routine in Germany. More than 300,000 images have been distributed among the communication partners in the last two years. Feedback and suggestions from the users influenced the system architecture by a great extent. The proposed and implemented system has been optimized to be as platform independent, open, and secure as possible.
Conflict of interest statement
The concepts of the CHILI system have been developed at the German Cancer Research Center in cooperation with the technology transfer company Steinbeis Transferzentrum Medizinische Informatik (STZ-MI) Heidelberg, Germany, which develops and markets the CHILI Software. Some of the authors are working as employess or consultants for that company.
Figures





Similar articles
-
[Research on testing the robustness of DICOM-e-mail secure teleradiology systems].Zhongguo Yi Liao Qi Xie Za Zhi. 2006 Jul;30(4):280-3, 252. Zhongguo Yi Liao Qi Xie Za Zhi. 2006. PMID: 17039939 Chinese.
-
Design and development of a secure DICOM-Network Attached Server.Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2006 Mar;81(3):197-202. doi: 10.1016/j.cmpb.2005.11.015. Epub 2006 Feb 28. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2006. PMID: 16503366
-
DICOM router: an open source toolbox for communication and correction of DICOM objects.Acad Radiol. 2005 Mar;12(3):385-92. doi: 10.1016/j.acra.2004.11.015. Acad Radiol. 2005. PMID: 15766700
-
[Clinical computer applications in the radiology department].Rinsho Byori. 1999 Feb;47(2):111-8. Rinsho Byori. 1999. PMID: 10097627 Review. Japanese.
-
A review of content-based image retrieval systems in medical applications-clinical benefits and future directions.Int J Med Inform. 2004 Feb;73(1):1-23. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmedinf.2003.11.024. Int J Med Inform. 2004. PMID: 15036075 Review.
Cited by
-
Therapy response in malignant pleural mesothelioma-role of MRI using RECIST, modified RECIST and volumetric approaches in comparison with CT.Eur Radiol. 2008 Aug;18(8):1635-43. doi: 10.1007/s00330-008-0918-9. Epub 2008 Mar 28. Eur Radiol. 2008. PMID: 18369634 Clinical Trial.
-
Imaging of aortopulmonary collateral arteries with high-resolution multidetector CT.Pediatr Radiol. 2006 Jun;36(6):502-9. doi: 10.1007/s00247-006-0143-0. Epub 2006 Mar 23. Pediatr Radiol. 2006. PMID: 16555039
-
Security of patient and study data associated with DICOM images when transferred using compact disc media.J Digit Imaging. 2009 Mar;22(1):65-70. doi: 10.1007/s10278-007-9068-x. Epub 2007 Aug 21. J Digit Imaging. 2009. PMID: 17710493 Free PMC article.
References
-
- American College of Radiology: ACR Standard for Teleradiology. Res. 35-1998. [1999 Jul 27]. http://www.acr.org/departments/stand_accred/standards/html_standards/htm....
-
- Engelmann U, Schröter A, Baur U, Baur HJ, Werner O, Schwab M, Wolsiffer K, Göransson B, Borälv E, Müller H, Meinzer HP. Teleradiology System MEDICUS. In: Lemke HU, editor. CAR '96: Computer Assisted Radiology. 10th International Symposium and Exhibition; Paris. Amsterdam: Elsevier; 1996. pp. 537–542.
-
- Engelmann U, Schröter A, Baur U, Werner O, Schwab M, Müller H, Bahner M, Meinzer HP. Second Generation Teleradiology. In: Lemke Heinz U, Vannier MW, Inamura Kiyonari., editors. CAR '97 - Computer Assisted Radiology and Surgery. Amsterdam: Elsevier Science Pub Co; 1997. Sep 1, pp. 632–637.
-
- Bahner ML, Engelmann U, Meinzer HP, van Kaick G. Design necessities for future teleradiology systems - Conclusion from a field test. Eur Radiol. 1997;(7 Suppl):S17.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

