Granule-dependent killing of Toxoplasma gondii by CD8+ T cells
- PMID: 11722643
- PMCID: PMC1783309
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2567.2001.01319.x
Granule-dependent killing of Toxoplasma gondii by CD8+ T cells
Abstract
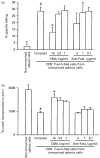
Immunization of mice with live bradyzoites of a low-virulent Beverley strain of Toxoplasma gondii has been shown to increase CD8+ T-cell mediated immunity against a highly virulent RH strain. We found that preimmunization with an RH homogenate further enhanced this immunity. Using this model, we investigated the mechanism of CD8+ T-cell mediated protection against T. gondii infection. Splenic cells from mice immunized with RH homogenate and live bradyzoites stimulated apoptosis of RH-infected J774A.1 macrophages in vitro, and at the same time, the immunization significantly suppressed the proliferation of parasites within macrophages, as assessed by measuring 3H-uracil uptake by the parasites. Splenic cells from the immunized mice produced larger amounts of interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma) than did naive splenic cells; however, the production of nitric oxide (NO) by RH-infected macrophages was not enhanced. The elimination of CD8+ T cells from splenic cells significantly reduced their inhibitory action on parasite proliferation as well as their cytotoxic activity against RH-infected macrophages, but it did not affect the production of IFN-gamma. Treatment of CD8+ T-enriched splenic cells from the immunized mice with concanamycin A, but not an anti-Fas ligand monoclonal antibody, significantly reduced their anti-proliferative and killing capabilities, suggesting that the CD8+ T cells induced by immunization with RH antigen and live bradyzoites of the Beverley strain may exert protection against T. gondii infection at least in part through granule-dependent cytotoxic activities.
Figures




References
-
- Scharton-Kersten TM, Wynn TA, Dnkers EY, Bala S, Grunvald E, Hieny S, Gazzinelli RT, Sher A. In the absence of endogenous IFN-γ, mice develop unimpaired IL-12 responses to Toxoplasma gondii while failing to control acute infection. J Immunol. 1996;157:4045–54. - PubMed
-
- Gazzinelli R, Xu Y, Hieny S, Cheever A, Sher A. Simultaneous depletion of CD4+ and CD8+ T lymphocytes is required to reactivated chronic infection with Toxoplasma gondii. J Immunol. 1992;149:175–80. - PubMed
-
- Gazzinelli RT, Hakim FT, Hieny S, Shearer GM, Sher A. Synergistic role of CD4+ and CD8+ T lymphocytes in IFN-γ production and protective immunity induced by and attenuates Toxoplasma gondii vaccine. J Immunol. 1991;146:286–92. - PubMed
-
- Suzuki Y, Remington JS. The effect of anti-IFN-γ antibody on the protective effect of LYT-2+ immune T cells against toxoplasmosis in mice. J Immunol. 1990;144:1954–6. - PubMed
-
- Suzuki Y, Orellana MA, Schreiber RD, Remington JS. Interferon-γ: the major mediator of resistance against toxoplasmosis in mice. Science. 1988;240:516–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

