The involvement of L-type Ca(2+) channels in the relaxant effects of the ATP-sensitive K(+) channel opener ZD6169 on pig urethral smooth muscle
- PMID: 11724757
- PMCID: PMC1573091
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0704408
The involvement of L-type Ca(2+) channels in the relaxant effects of the ATP-sensitive K(+) channel opener ZD6169 on pig urethral smooth muscle
Abstract
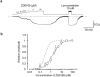
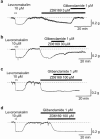
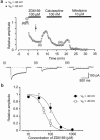
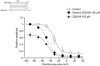
1. The effects of ZD6169, a novel ATP-sensitive K(+) channel (K(ATP) channel) opener, were investigated on membrane currents in isolated myocytes using patch-clamp techniques. Tension measurement was also performed to study the effects of ZD6169 on the resting tone of pig urethral smooth muscle. 2. Levcromakalim was more potent than ZD6169 in lowering the resting urethral tone. Relaxation induced by low concentrations of ZD6169 (< or =3 microM) was completely suppressed by additional application of glibenclamide (1 microM). In contrast, glibenclamide (1-10 microM) only partially inhibited the relaxation induced by higher concentrations of ZD6169 (> or = microM). 3. Bay K8644 (1 microM) reduced the maximum relaxation produced by ZD6169 (> or =10 microM). 4. In whole-cell configuration, ZD6169 suppressed the peak amplitude of voltage-dependent Ba(2+) currents in a concentration- and voltage-dependent manner, and at 100 microM, shifted the steady-state inactivation curve of the voltage-dependent Ba(2+) currents to the left at a holding potential of -90 mV. 5. In cell-attached configuration, open probability of unitary voltage-dependent Ba(2+) channels (27 pS, 90 mM Ba(2+)) was inhibited by 100 microM ZD6169 and by 10 microM nifedipine. 6. Reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction (RT - PCR) analysis revealed the presence of the transcript of the alpha(1C) subunit of L-type Ca(2+) channels in pig urethra. 7. These results demonstrate that ZD6169 causes urethral relaxation through two distinct mechanisms, activation of K(ATP) channels at lower concentrations and inhibition of voltage-dependent Ca(2+) channels at higher concentrations (about 10 microM).
Figures




Similar articles
-
Dual action of ZD6169, a novel K(+) channel opener, on ATP-sensitive K(+) channels in pig urethral myocytes.Br J Pharmacol. 2001 May;133(1):154-64. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0704042. Br J Pharmacol. 2001. PMID: 11325805 Free PMC article.
-
Multiple actions of U-37883A, an ATP-sensitive K+ channel blocker, on membrane currents in pig urethra.Eur J Pharmacol. 2005 Nov 7;524(1-3):1-10. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2005.08.048. Epub 2005 Oct 19. Eur J Pharmacol. 2005. PMID: 16242124
-
The effects of nifedipine and other calcium antagonists on the glibenclamide-sensitive K+ currents in smooth muscle cells from pig urethra.Br J Pharmacol. 1998 Apr;123(8):1601-8. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0701777. Br J Pharmacol. 1998. PMID: 9605567 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of levcromakalim and nucleoside diphosphates on glibenclamide-sensitive K+ channels in pig urethral myocytes.Br J Pharmacol. 1997 Apr;120(7):1229-40. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0701033. Br J Pharmacol. 1997. PMID: 9105697 Free PMC article.
-
Zeneca ZD6169 activates ATP-sensitive K+ channels in the urinary bladder of the guinea pig.Pharmacology. 1996 Sep;53(3):170-9. doi: 10.1159/000139428. Pharmacology. 1996. PMID: 8931102
Cited by
-
Prostatic relaxation induced by loperamide is reduced in spontaneously hypertensive rats.ScientificWorldJournal. 2012;2012:941685. doi: 10.1100/2012/941685. Epub 2012 May 3. ScientificWorldJournal. 2012. PMID: 22645476 Free PMC article.
-
The effects of flavoxate hydrochloride on voltage-dependent L-type Ca2+ currents in human urinary bladder.Br J Pharmacol. 2005 Sep;146(1):25-32. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0706284. Br J Pharmacol. 2005. PMID: 15965499 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative studies of AJG049, a novel Ca2+ channel antagonist, on voltage-dependent L-type Ca2+ currents in intestinal and vascular smooth muscle.Br J Pharmacol. 2006 Sep;149(2):155-62. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0706861. Epub 2006 Aug 14. Br J Pharmacol. 2006. PMID: 16921392 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of voltage-dependent Ba2+ currents in the guinea-pig gastric antrum by cyclic nucleotide-dependent pathways.Br J Pharmacol. 2005 Sep;146(1):129-38. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0706295. Br J Pharmacol. 2005. PMID: 15965497 Free PMC article.
-
Multiple effects of mefenamic acid on K(+) currents in smooth muscle cells from pig proximal urethra.Br J Pharmacol. 2003 Dec;140(8):1341-50. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0705524. Epub 2003 Nov 17. Br J Pharmacol. 2003. PMID: 14623761 Free PMC article.
References
-
- BOLTON T.B., PRESTWICH S.A., ZHOLOS A.V., GORDIENKO D.V. Excitation-contraction coupling in gastrointestinal and other smooth muscles. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 1999;61:85–115. - PubMed
-
- BUCKNER S.A., MILICIC I., DAZA A., DAVIS-TABER R., SCOTT V.E., SULLIVAN J.P., BRIONI J.D. Pharmacological and molecular analysis of ATP-sensitive K+ channels in the pig and human detrusor. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2000;400:287–295. - PubMed
-
- GOPALAKRISHNAN M., WHITEAKER K.L., MOLINARI E.J., DAVIS-TABER R., SCOTT V.E., SHIEH C.C., BUCKNER S.A., MILICIC I., CAIN J.C., POSTL S., SULLIVAN J.P., BRIONI J.D. Characterization of the ATP-sensitive potassium channels (KATP) expressed in guinea pig bladder smooth muscle cells. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1999;289:551–558. - PubMed
-
- HOWE B.B., HALTERMAN T.J., YOCHIM C.L., DO M.L., PETTINGER S.J., STOW R.B., OHNMACHT C.J., RUSSELL K., EMPFIELD J.R., TRAINOR D.A., BROWN F.J., KAU S.T. ZENECA ZD6169: A novel KATP channel opener with in vivo selectivity for urinary bladder. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1995;274:884–890. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

