Role of heparan sulfate as a tissue-specific regulator of FGF-4 and FGF receptor recognition
- PMID: 11724824
- PMCID: PMC2150861
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200106075
Role of heparan sulfate as a tissue-specific regulator of FGF-4 and FGF receptor recognition
Abstract
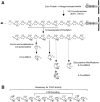
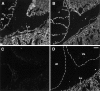
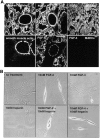
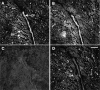
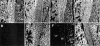
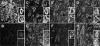
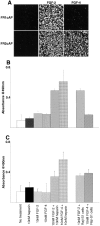
FGF signaling uses receptor tyrosine kinases that form high-affinity complexes with FGFs and heparan sulfate (HS) proteoglycans at the cell surface. It is hypothesized that assembly of these complexes requires simultaneous recognition of distinct sulfation patterns within the HS chain by FGF and the FGF receptor (FR), suggesting that tissue-specific HS synthesis may regulate FGF signaling. To address this, FGF-2 and FGF-4, and extracellular domain constructs of FR1-IIIc (FR1c) and FR2-IIIc (FR2c), were used to probe for tissue-specific HS in embryonic day 18 mouse embryos. Whereas FGF-2 binds HS ubiquitously, FGF-4 exhibits a restricted pattern, failing to bind HS in the heart and blood vessels and failing to activate signaling in mouse aortic endothelial cells. This suggests that FGF-4 seeks a specific HS sulfation pattern, distinct from that of FGF-2, which is not expressed in most vascular tissues. Additionally, whereas FR2c binds all FGF-4-HS complexes, FR1c fails to bind FGF-4-HS in most tissues, as well as in Raji-S1 cells expressing syndecan-1. Proliferation assays using BaF3 cells expressing either FR1c or FR2c support these results. This suggests that FGF and FR recognition of specific HS sulfation patterns is critical for the activation of FGF signaling, and that synthesis of these patterns is regulated during embryonic development.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The cell surface proteoglycan syndecan-1 mediates fibroblast growth factor-2 binding and activity.J Cell Physiol. 1998 Mar;174(3):310-21. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-4652(199803)174:3<310::AID-JCP5>3.0.CO;2-R. J Cell Physiol. 1998. PMID: 9462693
-
Fibroblast growth factor receptors 1 and 2 interact differently with heparin/heparan sulfate. Implications for dynamic assembly of a ternary signaling complex.J Biol Chem. 2002 Aug 9;277(32):28554-63. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111754200. Epub 2002 May 28. J Biol Chem. 2002. PMID: 12034712
-
Heparin differentially regulates the interaction of fibroblast growth factor-4 with FGF receptors 1 and 2.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1999 Oct 5;263(3):621-6. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1999.1434. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1999. PMID: 10512728
-
A protein canyon in the FGF-FGF receptor dimer selects from an à la carte menu of heparan sulfate motifs.Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2005 Oct;15(5):506-16. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2005.09.002. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2005. PMID: 16154740 Review.
-
Heparan sulfate fibroblast growth factor receptor complex: structure-function relationships.Mol Reprod Dev. 1994 Sep;39(1):69-81; discusison 81-2. doi: 10.1002/mrd.1080390112. Mol Reprod Dev. 1994. PMID: 7999363 Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular pathology of the fibroblast growth factor family.Hum Mutat. 2009 Sep;30(9):1245-55. doi: 10.1002/humu.21067. Hum Mutat. 2009. PMID: 19621416 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Changes in the expression patterns of the genes involved in the segregation and function of inner cell mass and trophectoderm lineages during porcine preimplantation development.J Reprod Dev. 2013;59(2):151-8. doi: 10.1262/jrd.2012-122. Epub 2012 Dec 20. J Reprod Dev. 2013. PMID: 23257836 Free PMC article.
-
Heparinoid Complex-Based Heparin-Binding Cytokines and Cell Delivery Carriers.Molecules. 2019 Dec 17;24(24):4630. doi: 10.3390/molecules24244630. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 31861225 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Proteoglycans as Immunomodulators of the Innate Immune Response to Lung Infection.J Histochem Cytochem. 2018 Apr;66(4):241-259. doi: 10.1369/0022155417751880. Epub 2018 Jan 12. J Histochem Cytochem. 2018. PMID: 29328866 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Application of Force to a Syndecan-4 Containing Complex With Thy-1-αVβ3 Integrin Accelerates Neurite Retraction.Front Mol Biosci. 2020 Sep 29;7:582257. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2020.582257. eCollection 2020. Front Mol Biosci. 2020. PMID: 33134319 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baird, A. 1994. Potential mechanisms regulating the extracellular activities of basic fibroblast growth factor (FGF-2). Mol. Reprod. Dev. 39:43–48. - PubMed
-
- Bastaki, M., E.E. Nelli, P. Dell'Era, M. Rusnati, M.P. Molinari-Tosatti, S. Parolini, R. Auerbach, L.P. Ruco, L. Possati, and M. Presta. 1997. Basic fibroblast growth factor-induced angiogenic phenotype in mouse endothelium. A study of aortic and microvascular endothelial cell lines. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 17:454–464. - PubMed
-
- Beckner, M.E. 1999. Factors promoting tumor angiogenesis. Cancer Invest. 17:594–623. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

