Comparative quantitation of cytomegalovirus (CMV) DNA in solid organ transplant recipients with CMV infection by using two high-throughput automated systems
- PMID: 11724864
- PMCID: PMC88568
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.39.12.4472-4476.2001
Comparative quantitation of cytomegalovirus (CMV) DNA in solid organ transplant recipients with CMV infection by using two high-throughput automated systems
Abstract
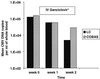
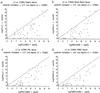
Cytomegalovirus (CMV) DNA quantitation in clinical specimens is progressively becoming a cornerstone in the diagnosis and management of CMV infection in the immunocompromised host. We evaluated two automated and reproducible PCR tests, the LightCycler (Roche Molecular Biochemicals, Indianapolis, Ind.) and the COBAS AMPLICOR CMV Monitor (Roche Diagnostics, Pleasanton, Calif.), for the detection of CMV DNA in blood samples from transplant recipients with CMV infection as determined by shell vial culture. Following a log transformation analysis, the mean CMV DNA in plasma (PL), whole blood (WB), peripheral blood leukocytes (PBL), and peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) using the LightCycler was 6.79 copies per ml, 7.23 copies per ml, 6.38 copies per 2 x 10(6) cells, and 6.27 copies per 2 x 10(6) cells, respectively. This compares to 7.86 copies per ml, 8.37 copies per ml, 7.59 copies per 2 x 10(6) cells, and 7.44 copies per 2 x 10(6) cells, respectively, using COBAS AMPLICOR CMV Monitor. While higher CMV DNA levels were observed for the various blood compartments analyzed using COBAS AMPLICOR CMV Monitor, a high degree of correlation was evident between the two automated systems (jackknife correlation r = PL 0.77 [95% confidence interval (CI); 0.64, 0.90], WB 0.77 [95% CI; 0.62, 0.92], PBL 0.77 [95% CI; 0.67, 0.88], and PBMC 0.81 [95% CI; 0.72, 0.89], all P < 0.001). Therefore, we conclude that either automated diagnostic system is accurate for CMV DNA quantitation.
Figures
References
-
- Abecassis M M, Koffron A J, Kaplan B, Buckingham M, Muldoon J P, Cribbins A J, Kaufman D B, Fryer J P, Stuart J, Stuart F P. The role of PCR in the diagnosis and management of CMV in solid organ recipients: what is the predictive value for the development of disease and should PCR be used to guide antiviral therapy? Transplantation. 1997;63:275–279. - PubMed
-
- DiDomenico N, Link H, Knobel R, Caratsch T, Weschler W, Loewy Z G, Rosenstraus M. COBAS AMPLICOR: fully automated RNA and DNA amplification and detection system for routine diagnostic PCR. Clin Chem. 1996;42:1915–1923. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

