Differences in clinical and laboratory diagnostic characteristics of penicilliosis marneffei in human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)- and non-HIV-infected patients
- PMID: 11724878
- PMCID: PMC88582
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.39.12.4535-4540.2001
Differences in clinical and laboratory diagnostic characteristics of penicilliosis marneffei in human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)- and non-HIV-infected patients
Abstract
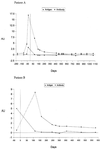
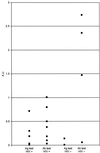
We compared the clinical and laboratory features of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)- and non-HIV-infected patients with penicilliosis marneffei. HIV-infected patients had a higher incidence of fungemia. A total of 85.7% of the HIV-negative patients had underlying diseases including hematologic malignancies or had received therapy with corticosteroids or cytotoxic agents. By a Penicillium marneffei-specific mannoprotein Mp1p enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, serum antigen titers were found to be higher in HIV-positive patients, whereas serum antibody levels were found to be higher in HIV-negative patients.
Figures
References
-
- Calera J A, Ovejero M C, Lopez-Medrano R, Lopez-Aragon R, Puente P, Leal F. The recombinant antigen ASPND1r from Aspergillus nidulans is specifically recognized by sera from patients with aspergilloma. Microbiology. 1998;144(Pt 2):561–567. - PubMed
-
- Chim C S, Fong C Y, Ma S K, Wong S S, Yuen K Y. Reactive hemophagocytic syndrome associated with Penicillium marneffei infection. Am J Med. 1998;104:196–197. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

