Ligand-induced signal transduction within heterodimeric GABA(B) receptor
- PMID: 11724957
- PMCID: PMC64735
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.251554798
Ligand-induced signal transduction within heterodimeric GABA(B) receptor
Abstract
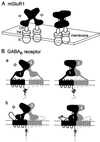
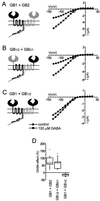
gamma-aminobutyric acid type B (GABA(B)) receptors, G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) for GABA, are obligate heterodimers of two homologous subunits, GB1 and GB2. Typical for family C GPCRs, the N termini of both GB1 and GB2 contain a domain with homology to bacterial periplasmic amino acid-binding proteins (PBPs), but only the GB1 PBP-like domain binds GABA. We found that both GB1 and GB2 extracellular N termini are required for normal coupling of GABA(B) receptors to their physiological effectors, G(i) and G protein-activated K(+) channels (GIRKs). Receptors with two GB2 N termini did not respond to GABA, whereas receptors with two GB1 N termini showed increased basal activity and responded to GABA with inhibition, rather than activation, of GIRK channels. This GABA-induced GIRK current inhibition depended on GABA binding to the chimeric GB(1/2) subunit (the GB1 N-terminal domain attached to the heptahelical domain of GB2), rather than the wild-type GB1 subunit. Interestingly, receptors with reciprocal exchange of N-terminal domains between the subunits were functionally indistinguishable from wild-type receptors. We also found that peptide linkers between GB1 and GB2 PBP-like domains and respective heptahelical domains could be altered without affecting receptor function. This finding suggests that other contacts between the PBP-like and heptahelical domains underlie ligand-induced signal transduction, a finding likely to be relevant for all family C GPCRs.
Figures
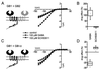
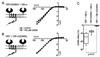
Similar articles
-
Function of GB1 and GB2 subunits in G protein coupling of GABA(B) receptors.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001 Dec 4;98(25):14649-54. doi: 10.1073/pnas.251554498. Epub 2001 Nov 27. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001. PMID: 11724956 Free PMC article.
-
Gamma-aminobutyric acid type B receptors with specific heterodimer composition and postsynaptic actions in hippocampal neurons are targets of anticonvulsant gabapentin action.Mol Pharmacol. 2001 Jan;59(1):144-52. Mol Pharmacol. 2001. PMID: 11125035
-
Desensitization of GABA(B) receptor signaling by formation of protein complexes of GABA(B2) subunit with GRK4 or GRK5.J Cell Physiol. 2007 Jan;210(1):237-45. doi: 10.1002/jcp.20863. J Cell Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17013811
-
GABAB receptor coupling to G-proteins and ion channels.Adv Pharmacol. 2010;58:123-47. doi: 10.1016/S1054-3589(10)58006-2. Adv Pharmacol. 2010. PMID: 20655481 Review.
-
Molecular mechanisms of GABA(B) receptor activation: new insights from the mechanism of action of CGP7930, a positive allosteric modulator.Biochem Soc Trans. 2004 Nov;32(Pt 5):871-2. doi: 10.1042/BST0320871. Biochem Soc Trans. 2004. PMID: 15494037 Review.
Cited by
-
Class C G protein-coupled receptors: reviving old couples with new partners.Biophys Rep. 2017;3(4):57-63. doi: 10.1007/s41048-017-0036-9. Epub 2017 Feb 28. Biophys Rep. 2017. PMID: 29238742 Free PMC article.
-
Closure of the Venus flytrap module of mGlu8 receptor and the activation process: Insights from mutations converting antagonists into agonists.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002 Aug 20;99(17):11097-102. doi: 10.1073/pnas.162138699. Epub 2002 Jul 31. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002. PMID: 12151600 Free PMC article.
-
Class A and C GPCR Dimers in Neurodegenerative Diseases.Curr Neuropharmacol. 2022;20(11):2081-2141. doi: 10.2174/1570159X20666220327221830. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35339177 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Determination of the minimal functional ligand-binding domain of the GABAB1b receptor.Biochem J. 2005 Mar 15;386(Pt 3):423-31. doi: 10.1042/BJ20040804. Biochem J. 2005. PMID: 15482257 Free PMC article.
-
The G protein-coupled receptor rhodopsin in the native membrane.FEBS Lett. 2004 Apr 30;564(3):281-288. doi: 10.1016/S0014-5793(04)00194-2. FEBS Lett. 2004. PMID: 15111110 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kaupmann K, Malitschek B, Schuler V, Heid J, Froestl W, Beck P, Mosbacher J, Bischoff S, Kulik A, Shigemoto R, et al. Nature (London) 1998;396:683–687. - PubMed
-
- Jones K A, Borowsky B, Tamm J A, Craig D A, Durkin M M, Dai M, Yao W J, Johnson M, Gunwaldsen C, Huang L Y, et al. Nature (London) 1998;396:674–679. - PubMed
-
- White J H, Wise A, Main M J, Green A, Fraser N J, Disney G H, Barnes A A, Emson P, Foord S M, Marshall F H. Nature (London) 1998;396:679–682. - PubMed
-
- Kuner R, Köhr G, Grünewald S, Eisenhardt G, Bach A, Kornau H C. Science. 1999;283:74–77. - PubMed
-
- Margeta-Mitrovic M, Jan Y N, Jan L Y. Neuron. 2000;27:97–106. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

